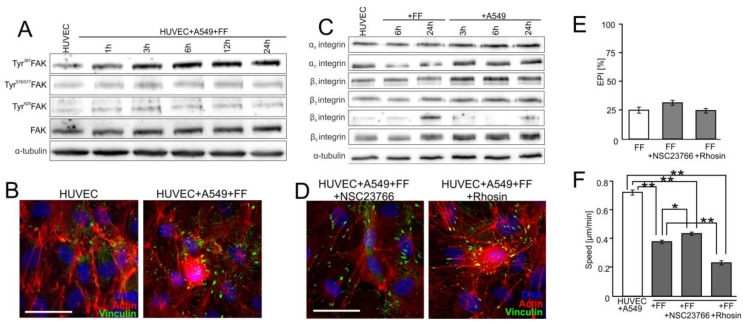
Figure 5.
FF directly attenuates HUVEC susceptibility to the activating signals generated by A549 cells. (A) HUVEC/A549 co-cultures were established as in Figure 1 and cultivated in the presence of 25 μM FF. Tyr397FAK, Tyr576/577FAK, and Tyr925FAK were analyzed at the indicated time points by immunoblotting and quantified by densitometry (Figure S5E). (B) Cytoskeletal architecture in HUVECs (Figure 3A) in A549/HUVEC co-cultures visualized by immunostaining in the absence (left) or presence of 25 μM FF (6 h; right). (C) HUVECs were cultivated in the presence of 25 μM FF or A549 cells and the levels of integrins were estimated at the indicated time points by immunoblotting and quantified by densitometry (Figure S5F). (D) The effect of NSC23766 (left) or Rhosin (right) on the cytoskeletal architecture of HUVECs cultured in the presence of A549 cells and 25 μM FF (see B for control). (E) Effect of NSC23766, Rhosin, and FF on the efficiency of A549 diapedesis (TransEndothelial Penetration; EPI), estimated after 6 h of A549/HUVEC co-culture. Transmigration of at least 200 A549 cells was analyzed for each group. (F) Effect of NSC23766 and Rhosin on the motility of proximal HUVECs analyzed in the presence of FF by time-lapse videomicroscopy. Error bars represent SEM. The statistical significance of the differences was tested with one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s HSD (E) or non-parametric Dunnett comparison (F); * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 against the control or # p < 0.05 against HUVEC/A549 control (see Figure 4B and Figure S5D). All results are representative of at least three independent experiments (n ≥ 3). Scale bar = 40 μm. Note that the inhibition of RhoA and Rac1 slightly counteracts FF-induced maturation of focal adhesions while inhibiting A549 diapedesis and HUVEC motility.