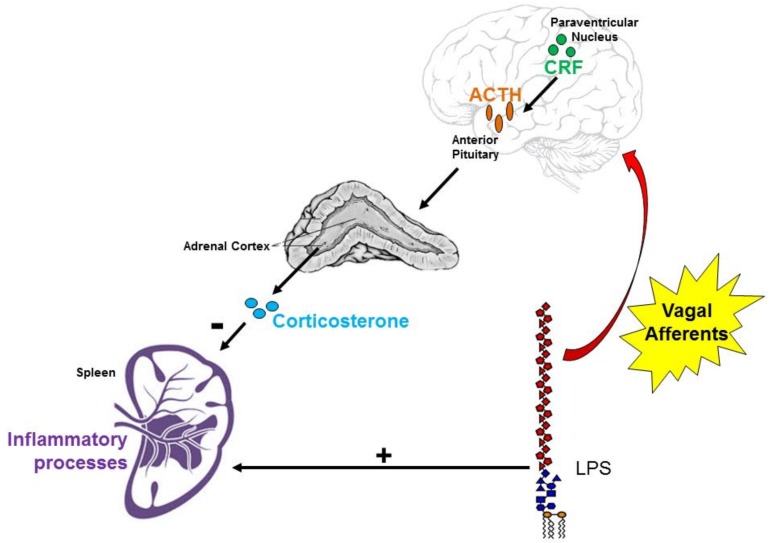
Figure 1.
The vagus nerve is a conduit between the brain and immune system. Vagal afferents transmit information regarding peripheral inflammatory processes (such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge, which also induces the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by splenic macrophages and other innate immune cells) to the nucleus tractus solitarius. This causes corticotropin releasing factor (CRF)-releasing parvocellular neurons in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus to prompt adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) release from the anterior pituitary. ACTH from the bloodstream then binds to receptors in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex to induce corticosterone release. Plasma corticosterone inhibits initiation of the inflammatory cascade.