Figure 2. DRMs lead to drug resistance/susceptibility in one linked transmission pair.
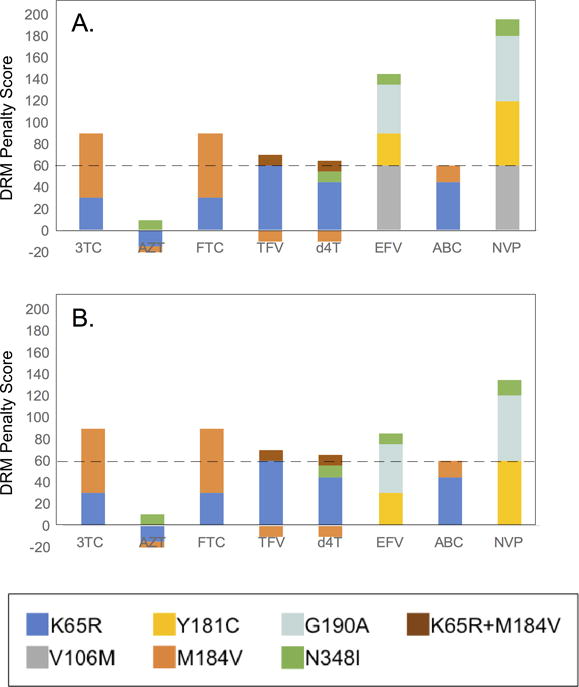
Transmitted drug resistance in one couple (MON 3076). Major drug resistance mutations (DRM) in transmitting/donor partner (A) and the seroconverter/recipient (B) partner at the time of transmission. Each DRM contributes to ARV resistance positively (values greater than 0) or negatively (values less than 0). The contribution of each DRM is estimated by penalty scores (generated by the Stanford HIV drug resistance database). The cumulative penalty score determines the level of drug resistance (between 0-9: susceptible; 10-14: potential low level resistance; 15-29, low level resistance; 30-59, intermediate resistance; ≥60, high level resistance).
