Figure 4. DRM result in treatment failure and subsequent transmission in Rwandan pairs.
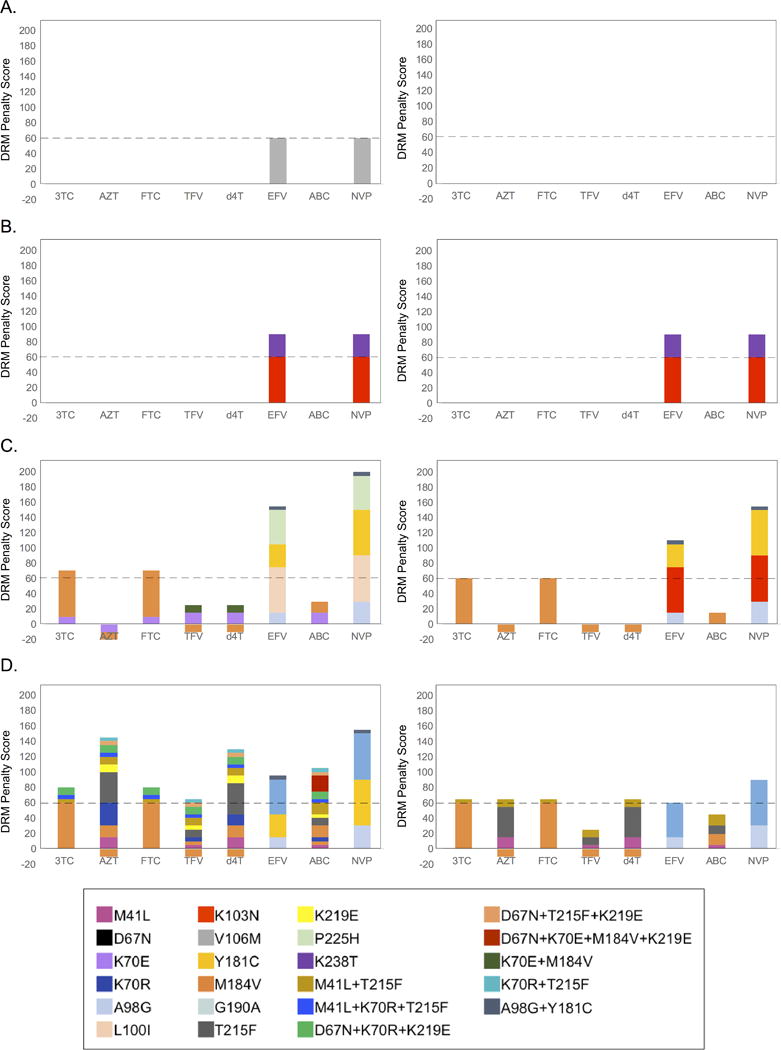
Pol sequences for donor and recipient partners were submitted to the Stanford HIV Drug Resistance database for the identification of potential DRM. Major DRM were detected in (A) BGO 003M (donor), (B) RUG 001F (donor) and RUG 001M (recipient), (C) COR 140F (recipient), and (D) COR 150M (donor) and COR 150F (recipient). The contribution of each DRM is estimated by penalty scores (a Stanford HIV drug resistance database measure). The cumulative penalty score determines the level of drug resistance (between 0-9: susceptible; 10-14: potential low level resistance; 15-29, low level resistance; 30-59, intermediate resistance; ≥60, high level resistance.
