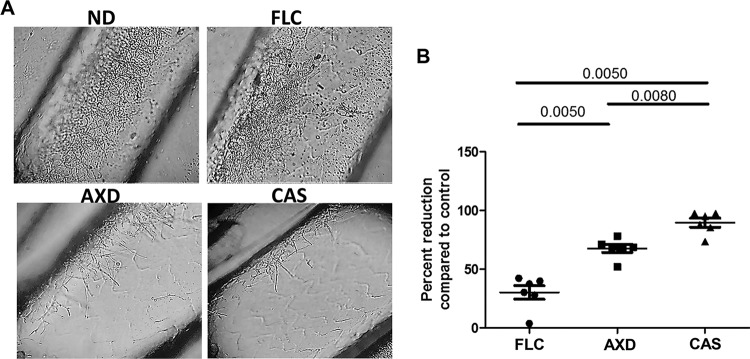
FIG 3.
Impact of AXD, fluconazole (FLC), and caspofungin (CAS) as lock therapy against C. albicans biofilm cells in an in vivo catheter model. (A) Biofilms were grown for 24 h followed by intraluminal drug treatment for 24 h. Following compound exposure, the catheters were removed for microscopy and CFU enumeration. Each of the four panels represent a 40× magnification under phase-contrast microscope. Panel columns: no drug treatment (ND), control biofilm treated with saline; FLC, 125-μg/ml fluconazole exposure; AXD, catheters exposed to AXD at 3 μg/ml; CAS, catheters exposed to 0.25 μg/ml caspofungin. (B) After ND or drug treatment, catheters were cut into pieces, vortexed, and sonicated to release adhered cells in sterile PBS, and dilutions of the suspension were plated on solid medium for CFU enumeration. Results are presented as percent biofilm reduction in drug-treated catheters compared to the untreated catheter biofilms and analyzed statistically by using a nonparametric t test. A P value of <0.05 is significant.