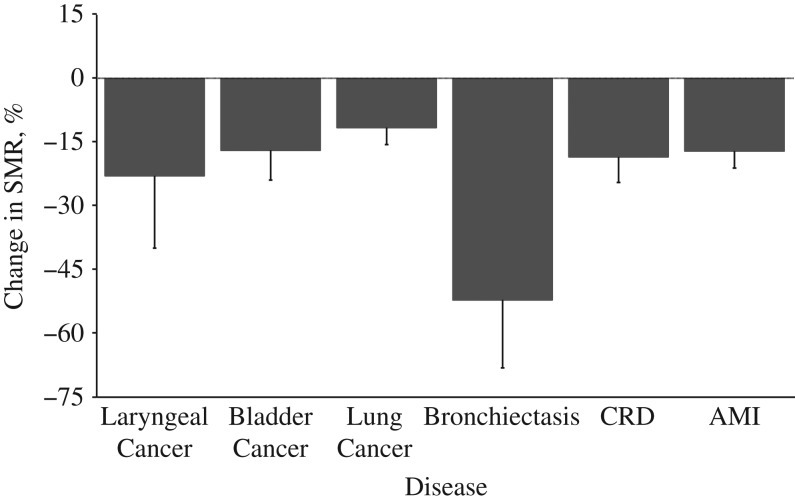
Figure 3.
Change in the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) for selected diseases per 10-year increase in age at first exposure to drinking water arsenic, Antofagasta, Chile, 2001–2010. Among cancers, the strongest relationship with age at first exposure was for cancer of the larynx, with a 23% reduction in the SMR for each 10-year increase in age (P for trend = 0.03). Among noncancer diseases, the strongest age relationship was for bronchiectasis, with a 49% reduction for each 10-year increase in age at first exposure (P for trend < 0.001). P values for trends are provided in Table 2. Bars, 95% confidence intervals. AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CRD, chronic renal disease.