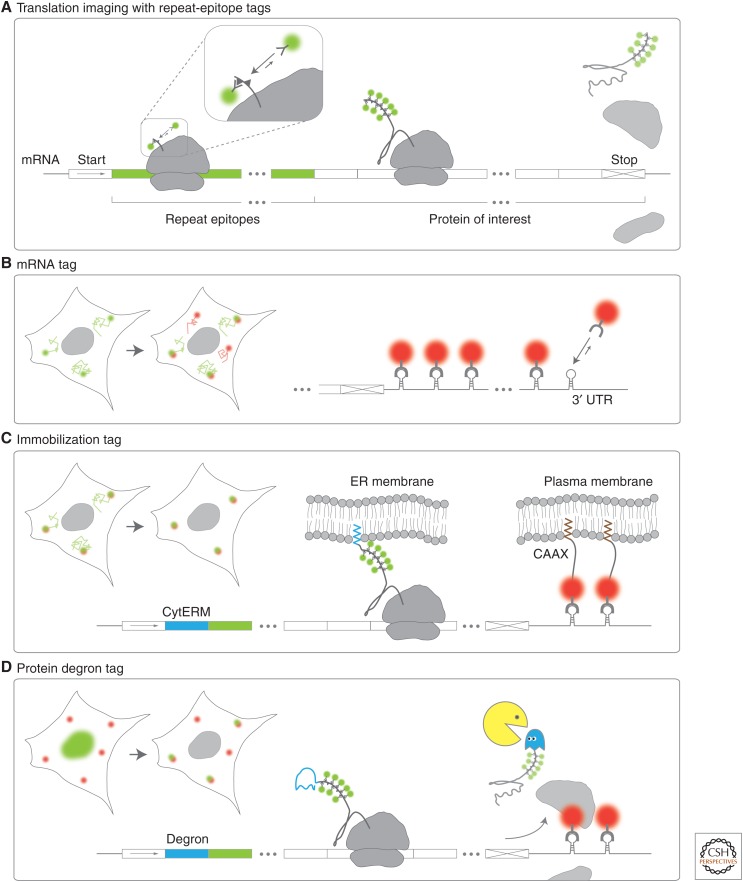
Figure 2.
Repeat-epitope and accessory tags for single-molecule imaging of mRNA translation. A schematic showing how repeat-epitope tags are used to visualize single translation sites in living cells. (A) Nascent peptides (small triangles) encoded by repeat epitopes (green mRNA) placed in the amino terminus of a protein of interest are co-translationally labeled by fluorescent antibody fragments (green spheres). (B) An mRNA tag can facilitate single mRNA translation imaging. Stem loops within the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of mRNA are co-transcriptionally labeled by coat proteins (red spheres). In combination with a repeat-epitope tag, translation sites are marked in green and red. (C) Immobilization tags can restrict the movement of mRNA so that translation sites can be tracked with less frequent imaging. The cytoplasmic end of an endoplasmic reticulum signal-anchor membrane protein (CytERM) tag (blue) embeds nascent chains into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) co-translationally, whereas a CAAX domain embeds transcripts with an mRNA tag into the plasma membrane via bound coat proteins (red spheres). (D) A degron (blue mRNA) encoded upstream of the repeat epitopes enhances the degradation of proteins, so nascent chains can be preferentially imaged (rather than mature proteins).