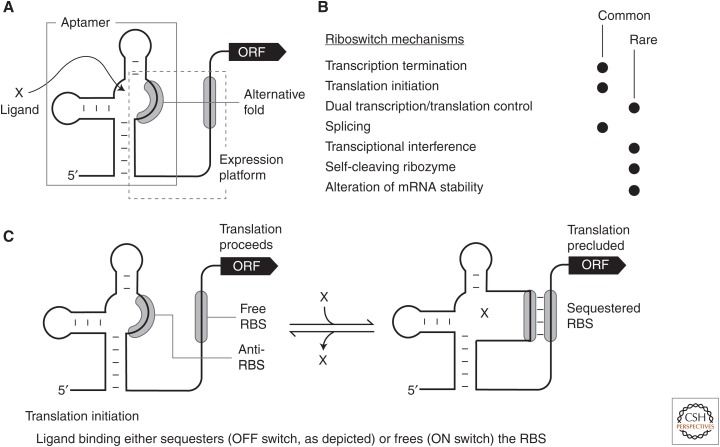
Figure 1.
Schematic representations of common riboswitch expression platform arrangements. (A) Riboswitches typically carry a single ligand-binding aptamer (gray box) located upstream of (and slightly overlapping) the expression platform (dashed box). Folding changes in the aptamer, brought about by ligand binding, cause folding changes in the expression platform to regulate gene expression by various mechanisms. (B) List of experimentally validated or predicted riboswitch gene-control mechanisms. Processes by which the mechanisms highlighted in bold italic font regulate translation and are discussed in the text. (C) Schematic representation of a riboswitch that permits translation in the absence of ligand (left), but inhibits translation when bound to ligand (right). In the model depicted, ligand binding sequesters the ribosome-binding site (RBS) and prevents ribosome binding to the messenger RNA (mRNA). Alternatively, some riboswitch RNAs liberate the RBS on ligand binding to promote ribosome binding and translation.