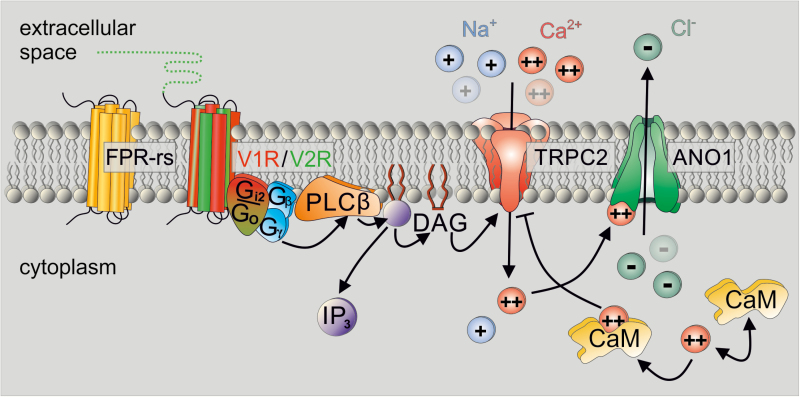
Figure 2.
Diagram illustrating the current model of VSN primary signal transduction. Known vomeronasal chemoreceptors—formyl peptide receptor-like (FPR-rs) proteins, V1R, and V2R receptors—initiate G protein–coupled phospholipase C type β (PLCβ) signaling that results in phosphoinositide turnover and elevations in both inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). Notably, a given VSN only expresses one member of either receptor family and, accordingly, either Gαi2 or Gαo. DAG-mediated Ca2+ entry via transient receptor potential canonical type 2 (TRPC2) channels underlies initial depolarization as well as gating of a Ca2+-activated Cl− channel (anoctamin1 [ANO1]). Bound to calmodulin (CaM), Ca2+ also triggers negative feedback inhibition of TRPC2.