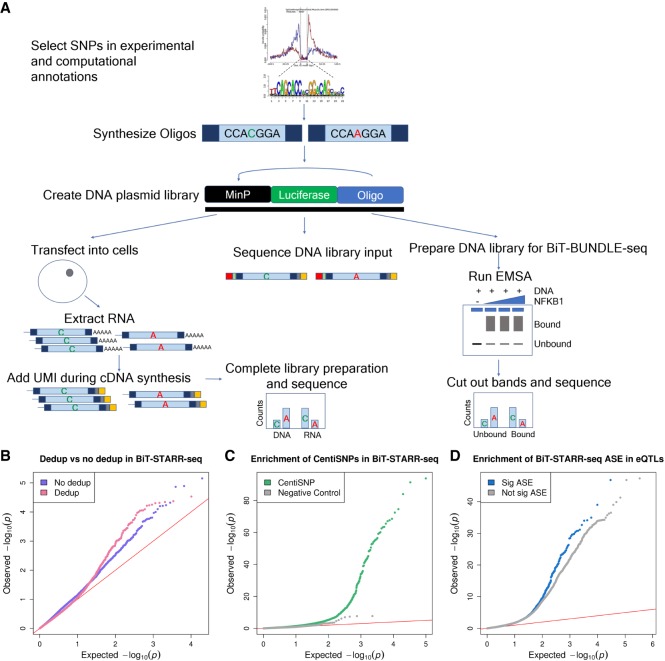
Figure 1.
BiT-STARR-seq and BiT-BUNDLE-seq identify regulatory variants in noncoding regions. (A) Experimental outline. Oligos targeting the regulatory regions of interest (and either reference or alternate alleles) are designed to contain, on their ends, 15 bp matching the sequencing primers used for Illumina NGS. The DNA library is used both in the BiT-STARR-seq and BiT-BUNDLE-seq experiments. UMIs are added during cDNA synthesis for the BiT-STARR-seq RNA-seq library and prior to PAGE in the BiT-BUNDLE-seq protocol. (B) QQplot depicting the P-value distributions from QuASAR-MPRA for a single experimental replicate processed without removing duplicates (purple) or after removing duplicates using the UMIs (pink). (C) QQplot depicting the P-value distributions from the ASE test performed using QuASAR-MPRA on all replicates after removing duplicates. CentiSNPs are in green (Moyerbrailean et al. 2016b), and SNPs in the negative control group are in gray. (D) QQplot depicting the P-value distributions for eQTLs from Nédélec et al. (2016). SNPs with significant ASE (FDR < 10%) are in blue, and not significant ASE are in gray.