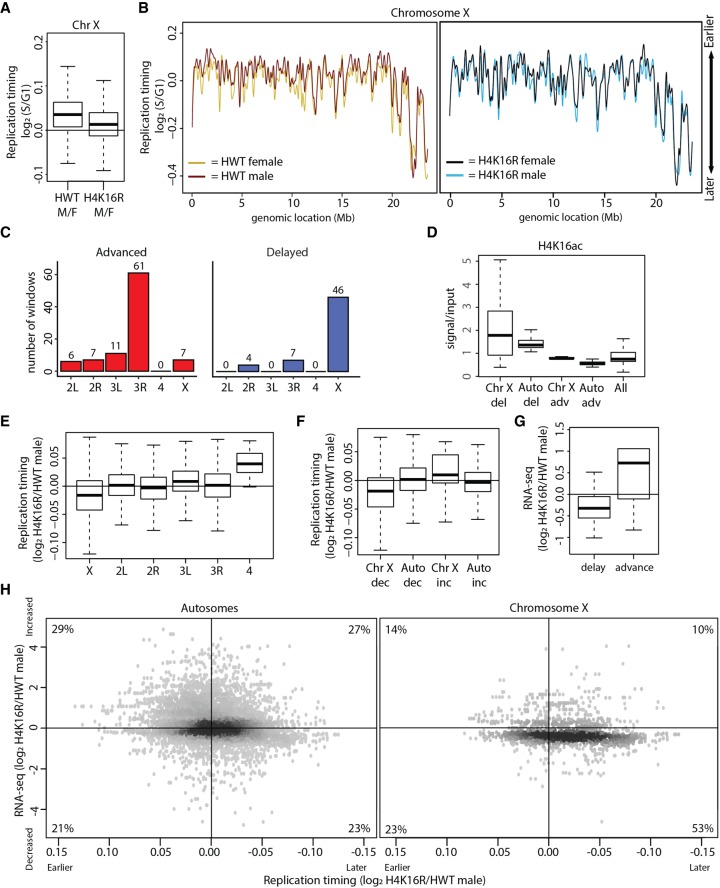
Figure 6.
H4K16R mutation reduces gene expression and delays replication of the male X Chromosome. (A) Box plot of HWT male/female and H4K16R male/female ratios of RT values (log2 S/G1) on Chr X. (B) LOESS regression line applied to log2 S/G1 averaged replicates from HWT female (yellow) and HWT male (maroon) and H4K16R female (black) and HWT male (blue) plotted across Chr X (100-kb windows, 10-kb slide). Note that the male X Chromosome generally replicates earlier in HWT, but not in H4K16R mutants. (C) Histogram of 10-kb windows with advanced (red) or delayed (blue) RT between H4K16R and HWT males on major chromosome scaffolds (P < 0.05; absolute log2 fold change > 0.1; limma). (D) Average enrichment of modENCODE H4K16ac signal from male third instar larvae at 10-kb windows of delayed (del) or advanced (adv) replication between H4K16R and HWT males on Chr X and autosomes (Auto) or at all 10-kb windows (GSE49497) (Celniker et al. 2009). (E) Box plot of the H4K16R/HWT ratio of male RT values (log2 S/G1) on all major chromosome scaffolds. (F) Box plot of the H4K16R/HWT ratio of male RT values (log2 S/G1) at 10-kb windows of decreased or increased RNA-seq signal on Chr X or autosomes (Auto) (P < 0.05). (G) Box plot of the H4K16R/HWT ratio of male RNA-seq signal at 10-kb windows of delayed or advanced RT (P < 0.05). (H) Heatscatter plot of the H4K16R/HWT ratio of male RT values (log2 S/G1) plotted versus the H4K16R/HWT ratio of male RNA-seq signal at all 10-kb windows across the autosomes (left) and Chr X (right). RNA-seq differences were determined based on the transcript with the lowest P-value across the 10-kb window. The percentage of 10-kb windows present in each quadrant is indicated.