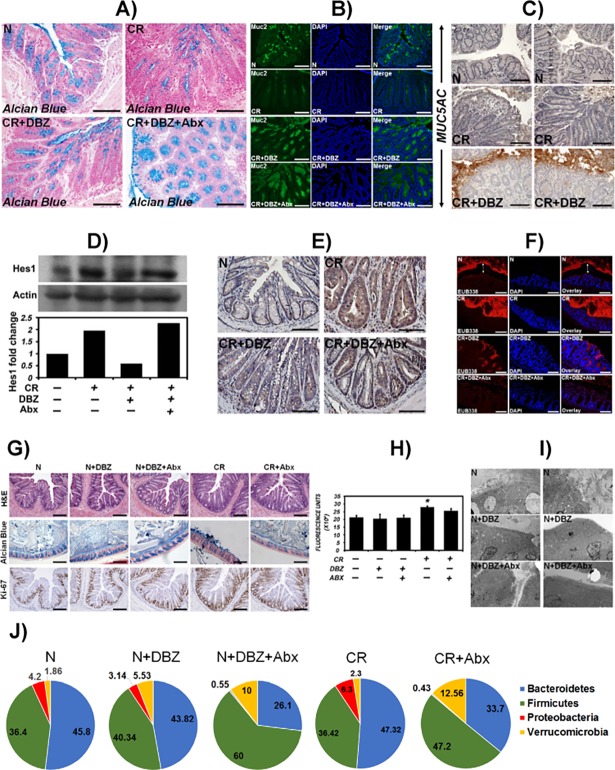
Fig 7. Proof-of-concept experiments to confirm Notch blockade in response to γ-secretase inhibitor, Dibenzazepine (DBZ).
NIH: Swiss mice were infected with CR and treated with DBZ, i.p. @ 10μmol/Kg body weight or DBZ+ antibiotics (Abx) (1g/l metronidazole and 0.2 g/l ciprofloxacin) for 10 days. A, B. Paraffin sections prepared from uninfected (N), CR-infected (CR), CR+DBZ-treated and CR+DBZ+Abx-treated mice were stained with Alcian blue (A) and Muc-2 (B) to detect goblet cells. C. Paraffin sections from uninfected (N), CR-infected (CR) and CR+DBZ-treated mice were stained for MUC5AC. Bars (A-C) = 150-200μm; n = 3 independent experiments. D. Western blot showing relative abundance of Hes-1 in crypt extracts prepared from the indicated groups. Bar graph shows fold change in Hes-1 levels (n = 1). E. Representative immuno-staining for Hes-1 in the sections prepared from the indicated groups. Bar = 125μm; n = 3 independent experiments. F. Representative fluorescence microscopy to detect bacteria in the unflushed and Carnoy-fixed colonic tissues of N, CR, CR+DBZ and CR+DBZ+Abx-treated mice via FISH using a general bacterial 16S probe (TexasRed-Eub338; Bar = 100μm; n = 10 mice/group). DAPI was used as counter-stain. Two-sided arrows represent the distance between the bacterial staining and the epithelial monolayer. G-J. Control experiments in uninfected (N) mice treated with DBZ or DBZ+Abx and CR-infected mice treated with Abx. Indicated analyses including H&E, Alcian Blue and Ki-67 staining (G; bar = 75μm), FITC-D measurement as fluorescence units (H; *p<0.05), electron microscopy (I) and 16S sequencing at the phyla level (J) were performed. n = 3 independent experiments.