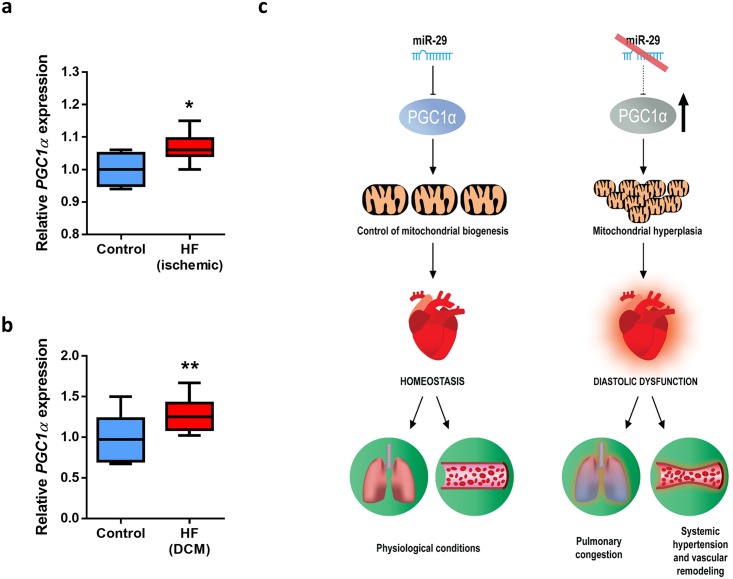
Fig 7. PGC1α is deregulated in HF patients.
(A) Relative expression of PGC1α in cardiac biopsies from 12 patients with ischemic HF and five biopsies from the non-infarcted zone from the same individuals (GEO accession number GSE26887) [48]. (B) Relative expression of PGC1α in left ventricle of 16 DCM patients and 10 normal individuals (GEO accession number GSE1145). (C) Model summarizing the functional and pathological relevance of the cardiometabolic miR-29/PGC1α axis. Under physiological conditions, mature miR-29 members regulate PGC1α and control mitochondrial homeostasis. However, the pathologic silencing of miR-29 leads to PGC1α up-regulation, and the increment in the expression of this transcriptional coactivator triggers mitochondrial biogenesis and hyperplasia. Large amounts of small mitochondria in cardiomyocytes may contribute to triggering diastolic dysfunction, systemic hypertension, pulmonary congestion, and vascular remodeling, resulting in heart failure and premature death. Original raw data can be found in S1 Data file. DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy; HF, heart failure.