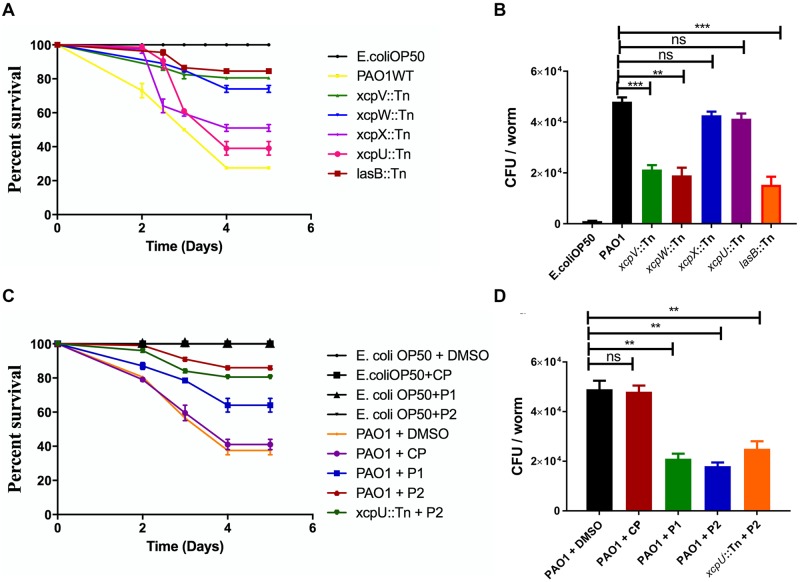
Fig 6. Effects of the structure-based peptides on C. elegans survival infected by P. aeruginosa.
(A) The T2SS is critical to the virulence of P. aeruginosa towards C. elegans. The Kaplan-Meier plot for the survival of C. elegans with infection of PAO1 and various mutants indicates that the viability of C. elegans increased when infected by xcpV, xcpW and lasB mutant strains. Assays were conducted at pH 7.3 with subsaturating (0.2 mM) PEP. I50 values correspond to the citrate or aspartate concentration that elicits 50% inhibition of AtPPC3 activity. All values in are plotted as means "S.E.M. of n = 4 separate experiments; where invisible the error bars are too small to be seen. (B) Bacterial CFU isolated from each infected worm. The reduction of CFU in xcpV, xcpW and lasB mutant strains indicates that the accumulation and virulence of P. aeruginosa have decreased. (C) Structure-based peptides increased the viability of P. aeruginosa- infected C. elegans. The Kaplan-Meier plot was established for C. elegans fed with either E. coli OP50 or P. aeruginosa in the absence or presence of structure-based peptides. ** P-value < 0.05 was adopted as statistically significant. ns: no significant difference. Structure-based peptides P1 and P2 have specifically affected virulence of P. aeruginosa and enhanced the viability of worms. (D) The level of accumulation of P. aeruginosa in C. elegans decreased in the presence of the inhibitory peptides.