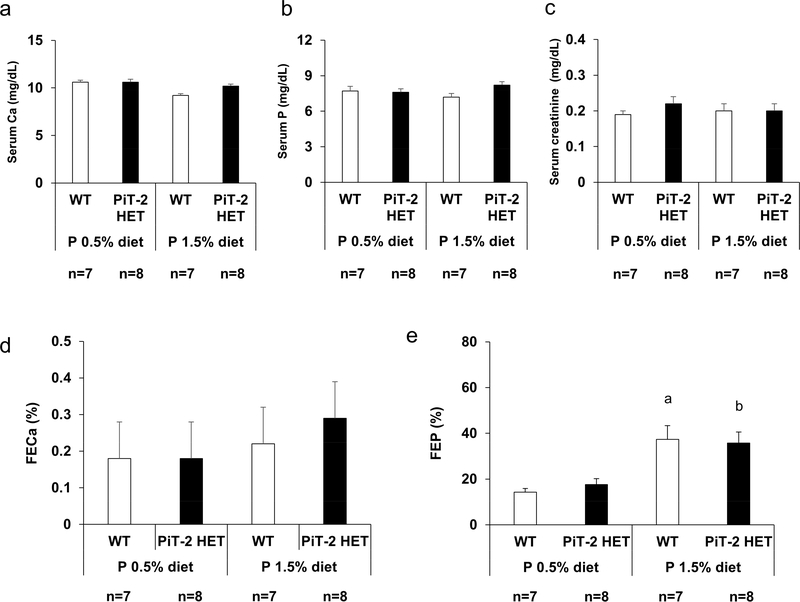
Figure 2 |. Impact of PiT-2 haploinsufficiency on renal phosphate handling under normal kidney function (metabolic cage study).
(a) Serum Ca level. (b) Serum P level. (c) Serum creatinine level. (d) FECa on either a 0.5% P diet or 1.5% P diet. (e) FEP on either a 0.5% P diet or 1.5% P diet. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=7–8) and compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer test. A two-tailed P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. aP<0.05 versus WT mice fed a 0.5% P diet. bP<0.05 versus PiT-2 HET mice fed a 0.5% P diet. ALP, alkaline phosphatase; Ca, calcium; FECa, fractional excretion of Ca; FEP, fractional excretion of P; P, phosphate; PiT-2 HET, PiT-2 heterozygous knockout; WT, wild-type.