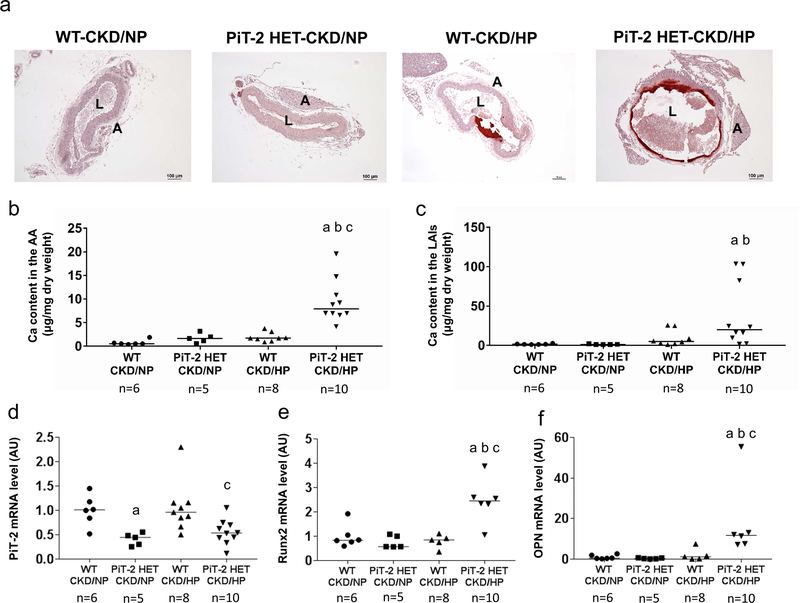
Figure 3 |. Effects of PiT-2 haplo-insufficiency on vascular calcification and calcification-related gene expression in CKD mice.
(a) Representative microphotograph of the abdominal aorta. Original magnification, x200, scale bar = 50 μm. (b) Calcium content in the AA. (c) Calcium content in the LAIs. Relative mRNA expression of (d) PiT-2, (e) Runx2, and (f) OPN in the aorta. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=6–10) and compared by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer test or Steel-Dwass test. A two-tailed P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. aP<0.05 versus WT-CKD/NP group. bP<0.05 versus PiT-2 HET-CKD/NP group. cP<0.05 versus WT-CKD/HP group. AA, aortic arch; AU, arbitrary unit; CKD, chronic kidney disease; HP, high phosphate; LAIs, lower abdominal aorta with bilateral common iliac arteries; NP, normal phosphate; OPN, osteopontin; Runx2, runt-related transcription factor 2; PiT-2 HET, PiT-2 heterozygous knockout; WT, wild-type.