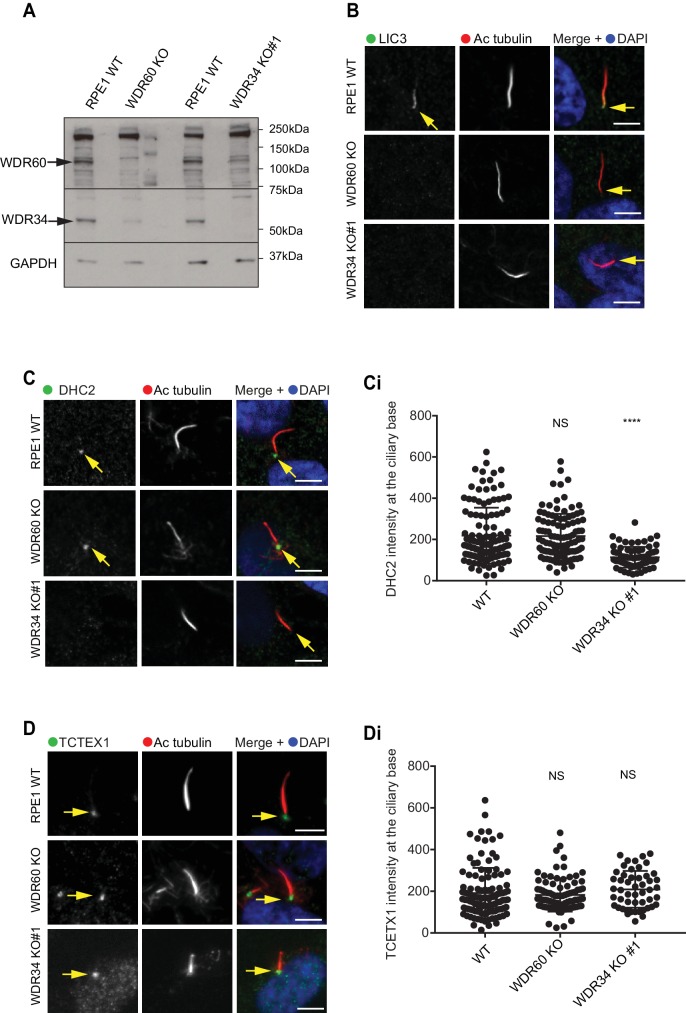
Figure 8. Dynein-2 assembly in primary cilium.
(A) Immunoblotting for WDR60 and WDR34 in WT, WDR34 KO#1 and WDR60 KO cells. Arrows indicate WDR34 and WDR60 proteins. (B) LIC3/DYNC2LI1 localization in the cilia of WT, WDR34 KO#1 and WDR60 KO cells. (C) DHC2/DYNC2H1 localization at the ciliary base in WT and KO cells. (Ci) Intensity quantification shows a reduction of DHC2/DYNC2H1 at the ciliary base in WDR34 KO#1 cells (n = 3, 120 WT, 106 WDR60 KO, and 71 WDR34 KO #1 cells quantified). (D) TCTEX1/DYNLT1 localizes at the ciliary base in WT and KO cells. (Di) Intensity quantification of TCTEX1/DYNLT1 at the ciliary base (n = 3 115 WT, 85 WDR60 KO, and 50 WDR34 KO#1 cells quantified). Mann-Whitney test, p-value: ****=<0.0001. Scale bars 5 μm. Arrows point to the ciliary base.
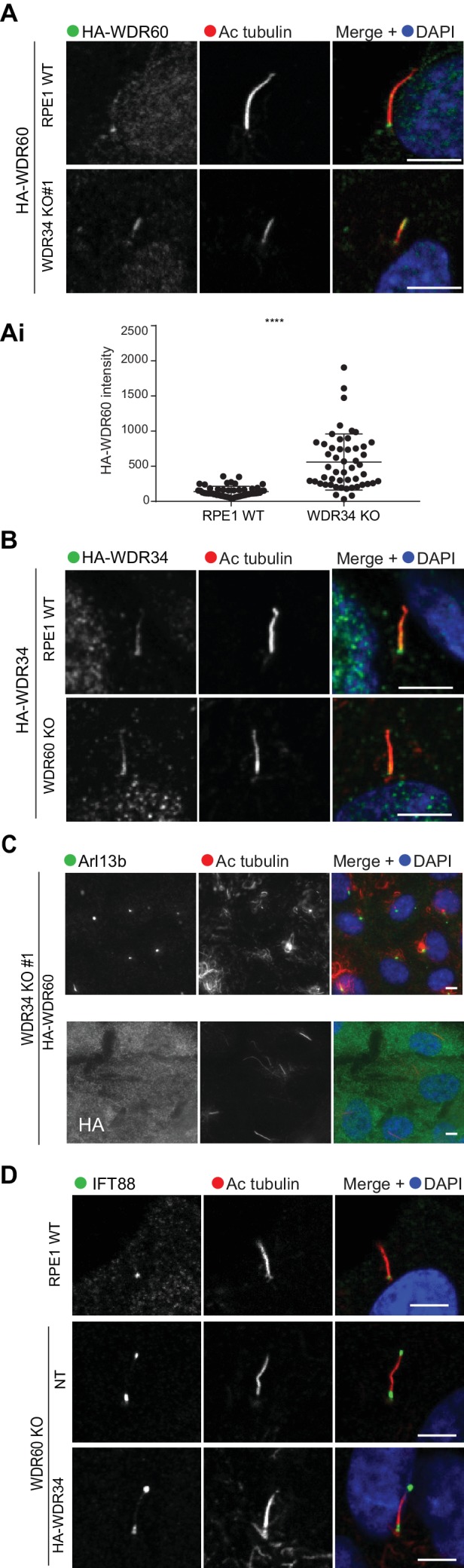
Figure 8—figure supplement 1. Overexpression of WDR34 cannot rescue WDR60 KO phenotype and vice versa.