Table 2.
An overview of common visual search experiments.
| Task properties | Inference | Sample scheme | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
B: solid white D: colored oriented lines T: colored or (and) oriented line Diff: orientation or (and) color |
Binding happens in early stages of visual processing. But the relationship between features are represented in lateral areas. |  |
Wolfe and Cave, 1999 |
|
B: solid black D: gray-oriented lines with wave-like homogenous pattern T: oriented line Diff: orientation, intensity, or both |
Contrast in feature of target and its local background induces saliency. |  |
Nothdurft, 1993 |
|
B: solid black D: gray squares T: gray square Diff: size, intensity, or both |
Size and intensity are functionally related. | 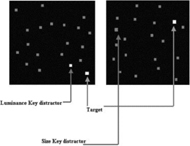 |
Huang and Pashler, 2005 |
|
B: solid black D: regular vertical colored line array (a column of lines are more salient than others in color or intensity) T: vertical broken line Diff: intensity or color with respect to the background except for the column in which the target is placed |
It is easier to find the target on the part of image that is salient due to color and intensity but not orientation. |  |
Jingling et al., 2013 |
|
B: grating D: circular gratings T: circular grating Diff: intensity, spatial frequency, and orientation |
Background properties (in addition to distractors) affect saliency. | 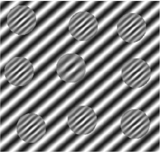 |
De Vries et al., 2013 |
|
B: surface texture D: not used T: small circle Diff: smoothness |
Proposing surface texture to study low-level features in attention |  |
Clarke et al., 2008 |
|
B: pixels with random color from two colors (R-G or B-Y) D: not used T: solid squares Diff: color which is chosen from one of two colors used in the background |
Yellowish targets in bluish background are more salient than other combinations. |  |
Wool et al., 2015 |
|
B: solid gray D: not used T: colored circles with various intensity Diff: hue and intensity |
Blue is the least salient color in gray background and needs more fixations to be detected. |  |
Etchebehere and Fedorovskaya, 2017 |
|
B: solid gray D: colored bars with various frequency T: colored bars with various frequency Diff: orientation and frequency |
Orientation attracts more attention than spatial frequency. |  |
Phillips et al., 2006 |
B, D, T, and Diff stand for background, distractors, target, and difference between target and distractors, respectively.
