Table 3.
An overview of common texture segmentation experiments.
| Task properties | Inference | Sample scheme | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
B: solid black (white) D: oriented (randomly) colored lines with a predefined texture T: not used Diff: not defined |
Neurons in primary visual cortex answer to saliency of preferred feature rather than the feature itself. | 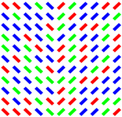 |
Jingling and Zhaoping, 2006 Zhaoping and May, 2007 |
|
B: basket texture background (textures are different in spatial frequency, orientation or both) D: not used T: not used Diff: not defined |
Texture segmentation is easier considering contrast in multiple features in comparison with contrast in only one feature. |  |
Bach et al., 2000 |
|
B: solid white D: black dots (a group of them were smaller or larger than others) T: not used Diff: not defined |
Infants in the first year are able to detect saliency in high degree. In third and fourth years of life, they are sensitive enough to get lower degree of saliency as well. |  |
Sireteanu et al., 2005 |
B, D, T, and Diff stand for background, distractors, target, and difference between target and distractors, respectively.
