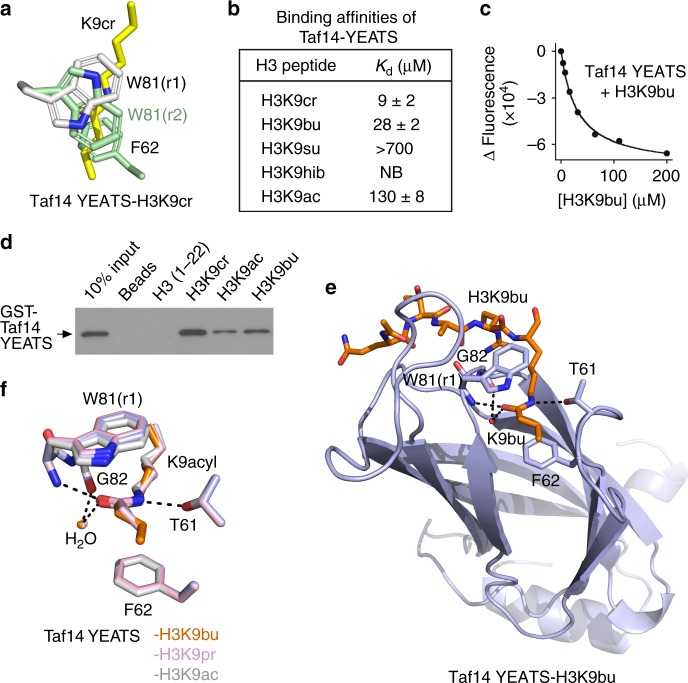
Fig. 1.
Structural insight into the selectivity of Taf14-YEATS. a Crotonylated lysine (yellow) is sandwiched between W81 and F62 in the complex of Taf14-YEATS with H3K9cr. W81 adopts two conformations, rotamer 1 (light gray) and rotamer 2 (green). b Binding affinities of Taf14-YEATS to the indicated histone peptides, as measured by fluorescence (cr, bu, ac) or NMR (su, hib). Values represent the average of three separate experiments (two for H3K9ac) with error calculated as the SD between the runs. The enhancement in selectivity of Taf14-YEATS to crotonyllysine is comparable to the enhancement in selectivity of other well-recognized epigenetic readers, such as DPFs8,11. c Representative binding curves used to determine Kd by tryptophan fluorescence. d Peptide pulldown assays for Taf14-YEATS using indicated histone H3 peptides. e The ribbon diagram of the Taf14-YEATS:H3K9bu complex. Dashed lines and red sphere represent hydrogen bonds and a water molecule, respectively. The YEATS domain is colored lavender and H3K9bu peptide is colored orange. Residues of the YEATS domain involved in the binding of K9bu are labeled. f Structural overlay of the acyllysine binding sites in the Taf14-YEATS:H3K9bu (lavender/orange), Taf14-YEATS:H3K9pr (pink), and Taf14-YEATS:H3K9ac14 (gray) complexes