Fig. 2.
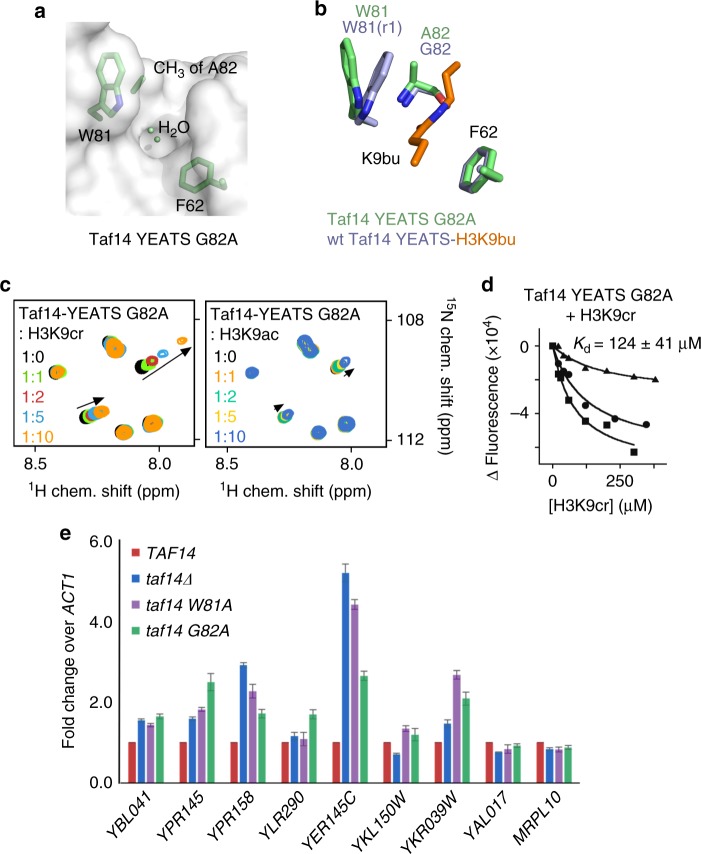
Engineering the Taf14-YEATS-based reader of H3K9cr. a Surface view of the Taf14-YEATS G82A mutant structure in the apo-state. The side chains of W81, A82, and F62 are shown as green sticks. b Structural overlay of the acyllysine-binding site in the Taf14-YEATS:H3K9bu (lavender/orange) complex and the apo state of Taf14-YEATS G82A (green). c Superimposed 1H,15N HSQC spectra of uniformly 15N-labeled G82A mutant of Taf14-YEATS recorded while the indicated peptides were added stepwise. The spectra are color coded according to the protein:peptide molar ratio. d Binding curves used to determine Kd of taf14-YEATS G82A by tryptophan fluorescence. e Real-time qPCR analysis of various transcripts in the wild-type strain, TAF14 delete strain, and taf14 mutant strains. The mean ± SD are calculated from three biological replicates