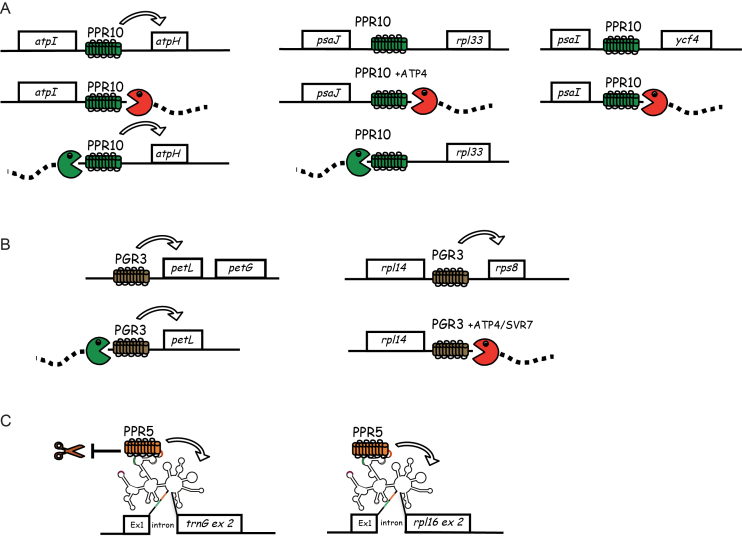
Figure 6.
Summary of the known functions of PPR10 (A), PGR3 (B) and PPR5 (C). See text for details. Arrows indicate an enhancement of translational efficiency (PPR10, PGR3) or RNA splicing (PPR5). RIP-seq data suggest that Zm-PGR3 may also interact weakly in the atpF-atpA intergenic region and possibly with a transcript related to the 23S rRNA. The diagrammed binding sites for PPR10, PGR3 and PPR5 are supported by RNA coimmunoprecipitation and/or in vitro RNA-binding assays. However, the effects of ATP4/SVR7 have not been shown to result from direct interaction with RNA. The fact that Zm-PGR3 mutants have a much more severe plastid ribosome deficiency than does Arabidopsis pgr3 implies that Zm-PGR3 has an as yet unidentified target involved in ribosome biogenesis. The RIP-seq data for Zm-PGR3 (Supplementary Figure S3) suggest that this might involve an interaction with 23S rRNA or a precursor thereof.