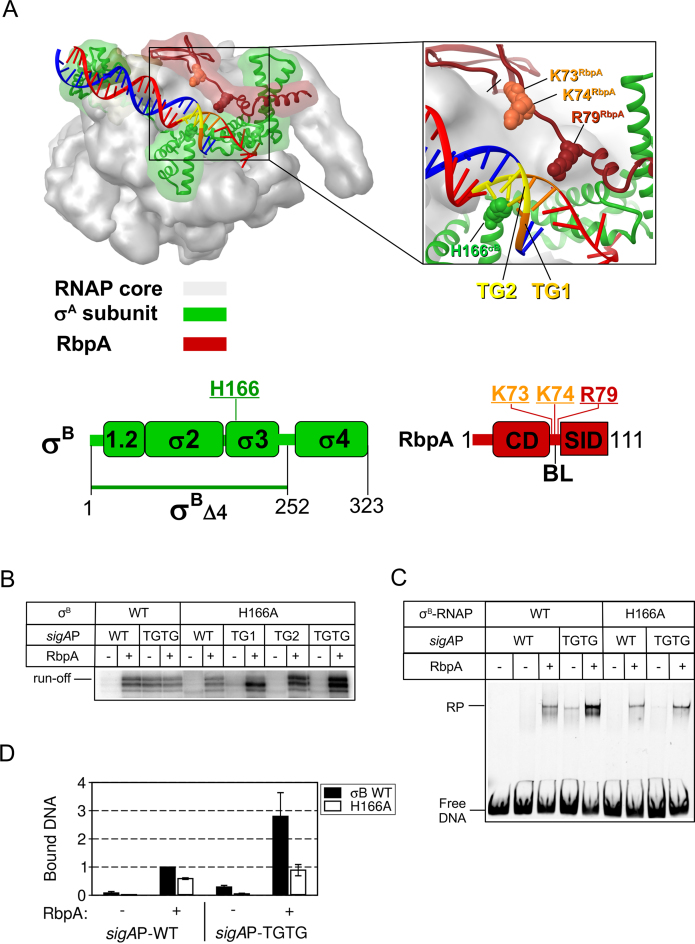
Figure 4.
The substitution H166A in region 3 of σB abolishes MtbRNAP interaction at the extended −10 motif. (A) Structural model of Mycobacterium smegmatis RNAP in complex with RbpA and promoter DNA (PDB code: 5TW1). Red ribbon, RbpA; green ribbon, σA subunit; gray semitransparent molecular surface, RNAP core; blue, DNA template strand; red, DNA non-template strand; orange, TG1-motif (T-15G-14); yellow, TG2-motif (T-17G-16). Residues in σB (H166) and RbpA (K73, K74, R79) that were mutated are shown in CPK rendering. Schematic representations of the RbpA and σB domains are shown at the bottom. The positions of the mutated residues are indicated. (B) Run-off [32P]-RNA products synthesized in run-off transcription assays using sigAP promoter derivatives in the presence or not of RbpA. (C) EMSA analysis of promoter complex formation by σB-MtbRNAP and fluorescein-labeled sigAP promoter variants. Complexes were resolved in native 5% PAGE. (D) Quantification of the experiment shown in panel C (mean values ± SE of two experiments).