Figure 4.
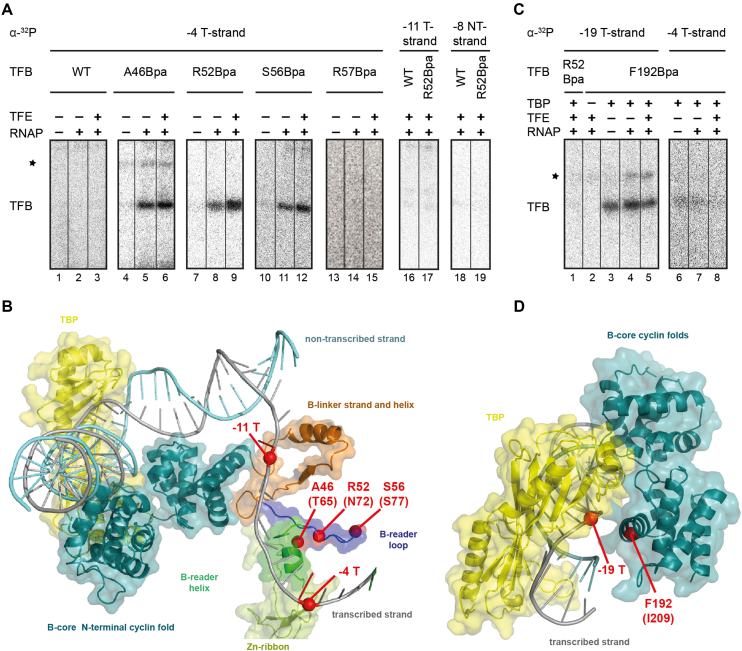
Specific crosslinks of TFB B-reader and TFB core Bpa-variants in the PIC. (A) TFB WT, A46Bpa, R52Bpa, S56Bpa and R57Bpa were used in crosslinking reactions together with a gdh-C6 DNA template radiolabeled at position -4 T (lanes 1–15). The TBP/TFB/DNA-complexes for each variant are represented in the first lanes and the open complexes in the second lanes, respectively. TFE was additionally present in the samples as indicated. A radioactive signal was observed on the 12% SDS-PAGE at a size of 37 kDa, which is the result of a covalent bond between TFB and the radiolabeled DNA. Other signals appear and are marked with an asterisk, but they are not factor specific, indicating an unspecific signal. TFB WT and R52Bpa show no crosslinking signal using a ghd-C6 cassette radiolabeled at position -11 on the T-strand (lanes 16 and 17) or at position –8 on the NT-strand (lanes 18 and 19). (B) Postulated eukaryotic yeast open complex model (PDB:3K1F; (22)). TBP is coloured in yellow and TFB domains are depicted in different colors (B-core in cyan; B-reader helix in green, B-reader loop in blue, B-linker in brown) whereas RNAP is excluded. TFB-Bpa positions and radiolabeled sites are shown as red dots. (C) The TFB B-core variant F192Bpa was used in crosslinking reactions together with gdh-C6 labeled at -19 (lanes 2 to 5) or –4 (lanes 6–8) on the T-strand. Specific crosslinks to position -19 T were observed in the ternary complex and the PIC without and with TFE. TFB R52Bpa did not crosslink to position -19 T (lane 1). Unspecific signals are marked with an asterisk. (D) Crystal structure of the TFB–TBP–DNA complex from P. woesei (PDB: 1AIS; (20)). The TFB B-core is shown in cyan), TBP in yellow and the DNA containing a TATA-bix in grey (20). Amino acid F192 and DNA position –19 are indicated by red dots.