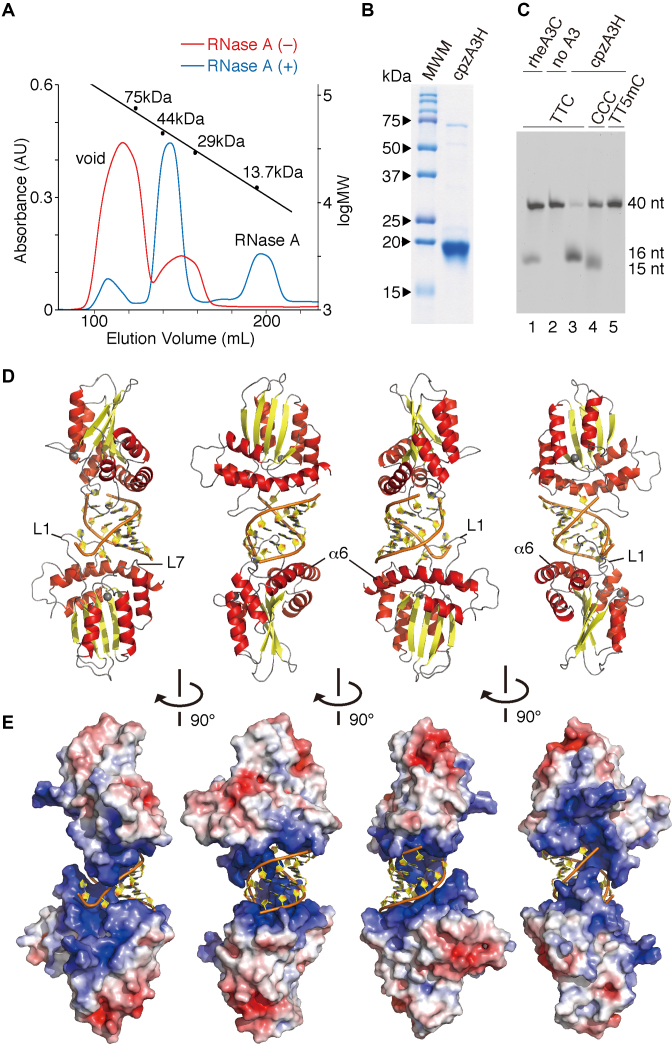
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of the cpzA3H dimer with an RNA duplex. (A) Gel filtration Superdex 75 elution profile of cpzA3H with (blue) or without (red) RNase A treatment. The standard MW marker proteins conalbumin (75 kDa), ovalbumin (44 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa) and RNase A (13.7 kDa) were used. (B) Gel image of purified cpzA3H stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250; MWM, MW marker. (C) Deamination activity of cpzA3H. Forty-nucleotide ssDNA substrates containing TTC (lanes 1, 2 and 3), the CCC (lane 4) or the TT5mC (lane 5) motifs were used in the UDG-dependent deamination assay. The recombinant protein rhesus macaque A3C (rheA3C) (lane 1) was used as a control; 5mC, 5-methylcytosine. (D) Ribbon and (E) electrostatic surface representations of cpzA3H seen in four rotated views. The ribbons are colored according to the secondary structures: α-helices (red); β-strands (yellow); loops (gray) and dsRNA (orange/yellow). Coordinated zinc ions are represented as navy spheres. The loops 1 and 7 and the α6 helix in chain A are indicated as L1, L7 and α6, respectively. The accessible surface area of cpzA3H is colored according to the calculated electrostatic potential from –5.0 kT/e (red) to +5.0 kT/e (blue).