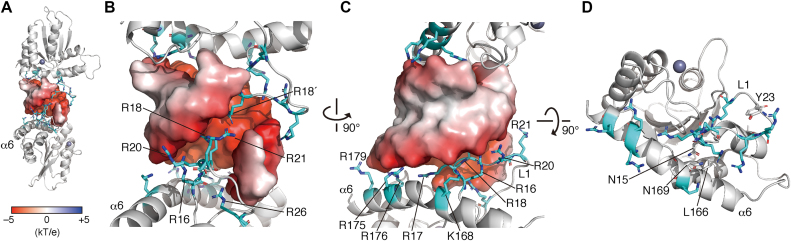
Figure 4.
Roles of A3H loop 1 (L1) and the α6 helix (α6) in the interaction with dsRNA. (A) RNA–duplex interaction interfaces formed by positively charged cpzA3H residues. The overall complex structure is represented with gray ribbons (cpzA3H) and an electrostatic surface (RNA). The basic residues involved in the RNA interaction are represented with cyan sticks. (B) Enlarged view of the interaction site between L1 and dsRNA. Basic residues R17, R18, R20 and R21 of L1 protrude into the negatively charged major groove of dsRNA. (C) Basic residues of L1 and α6 are aligned along the curvature of the RNA phosphate backbone. (D) The α6 position is fixed via the formation of a hydrogen bond between the L1 stem N15 (gray stick) and the α6 L166. The structure is shown without dsRNA is represented.