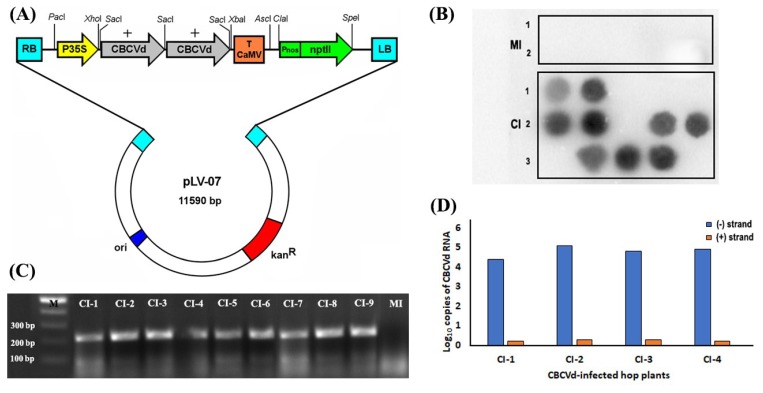
Figure 1.
Construction of Citrus bark cracking viroid (CBCVd)-infectious construct and CBCVd detection and quantification: (A) Schematic diagram of a plasmid including the CBCVd (+) dimer created by cDNA cloning in SacI restriction site. The CBCVd (+) dimer was re-cloned from pPCR-Script to XhoI–XbaI sites of intermediary vector pLV-68. Finally, modified expression cassette containing CaMV 35S promoter, viroid cDNA and CaMV terminator was cloned into PacI and AscI sites of the plasmid pLV-07. ori: origin of replication; kanR: kanamycin resistance gene; RB: left border of T-DNA; RB: right border of T-DNA; T CaMV: terminator from Cauliflower mosaic virus; Pnos: nopalin synthase promoter; nptII, Neomycin phosphotransferase II; (B) dot blot hybridization analysis of a [32P]-dCTP-labeled CBCVd cRNA probe to total nucleic acids isolated from mock inoculated (MI) and CBCVd-infected (CI) leaves of hop; (C) agarose gel electrophoresis analysis of mRT-PCR reaction for CBCVd-infected (CI-1 to CI-9) and mock inoculated (MI) leaves of hop after dormancy; (D) strand-specific real-time RT-qPCR analysis of reverse transcribed (+) or (−) CBCVd strands of CBCVd-infected hop plants after dormancy.