FIG 3.
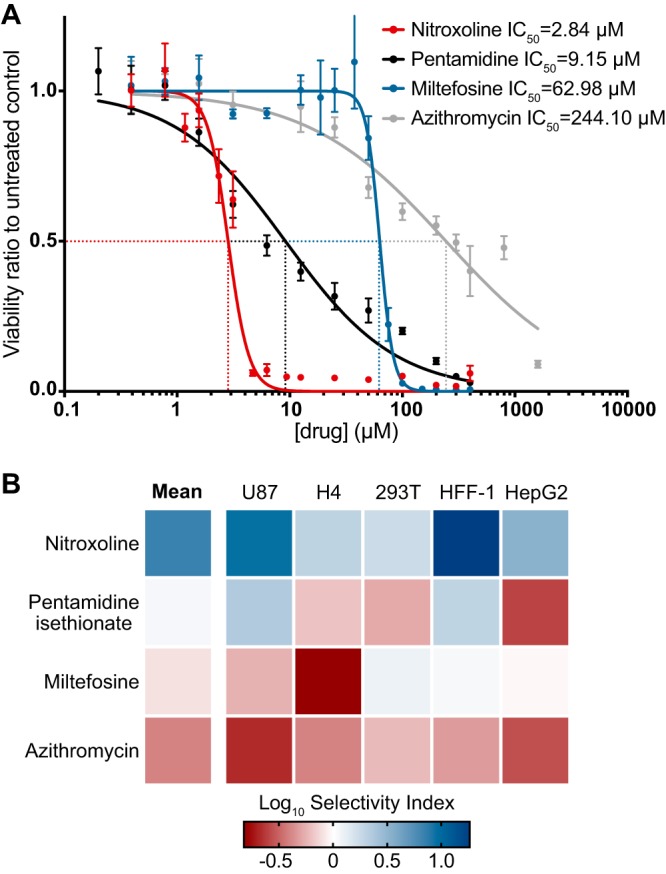
Potency and selectivity for inhibition of B. mandrillaris viability by nitroxoline, pentamidine isethionate, miltefosine, and azithromycin. (A) Dose-response curves show the effect of nitroxoline (red), pentamidine isethionate (black), miltefosine (blue), and azithromycin (gray) on the viability of B. mandrillaris trophozoite populations following 72 h of treatment. Data points represent means and standard errors of results from at least three independent biological replicates. Nitroxoline was the most potent inhibitor of B. mandrillaris viability, with an IC50 of 2.84 µM. (B) Heat map showing the Log10 selectivity index (human cell CC50/B. mandrillaris IC50) for nitroxoline, pentamidine, isethionate, miltefosine, and azithromycin calculated from the ratio of human cell CC50 to B. mandrillaris IC50. Nitroxoline exhibited the greatest mean Log10 selectivity index at 0.832 and was the only drug with a positive Log10 selectivity index (comparing B. mandrillaris inhibition to the results from all cell lines tested).
