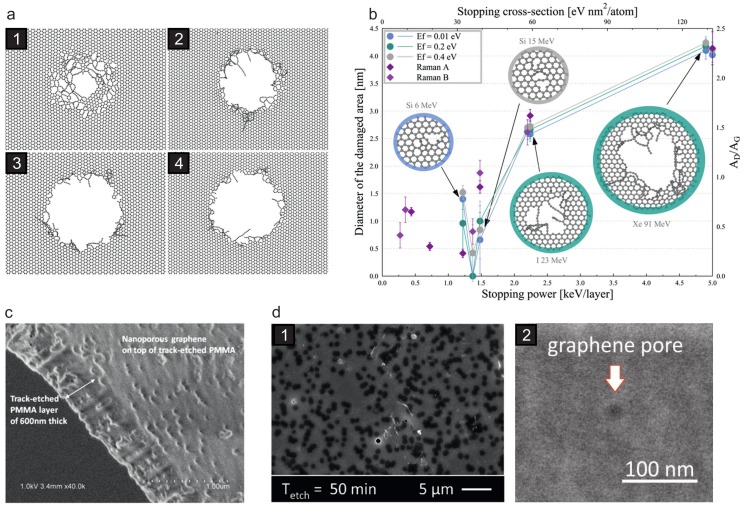
Figure 9.
Pore creation in supported and suspended graphene by SHI irradiation. (a,b) MD simulations of SHI irradiation of graphene. (a) Results for graphene on a SiO substrate. Large pores can be created by individual impacts, the size of which can be controlled via the electronic stopping of the projectile. Data is shown for values of (1) 6.5 keV/nm, (2) 8 keV/nm, (3) 10 keV/nm, (4) 12 keV/nm. Only graphene is shown for clarity. Reprinted from from Ref. [117], Copyright (2015), with permission from Elsevier. (b) Results for graphene without substrate. Again, the pore size increases with increasing electronic stopping. Reprinted from Ref. [124], Copyright (2017), with permission from Elsevier. (c,d) Scanning electron microscope images from graphene/polymer membranes which have been irradiated with SHI and subsequently etched. Composite membranes with nanometer-sized pores in the graphene can be obtained in this way. (c) Reprinted from from Ref. [126], Copyright (2016), with permission from Elsevier; (d) Reproduced from Ref. [127] with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.