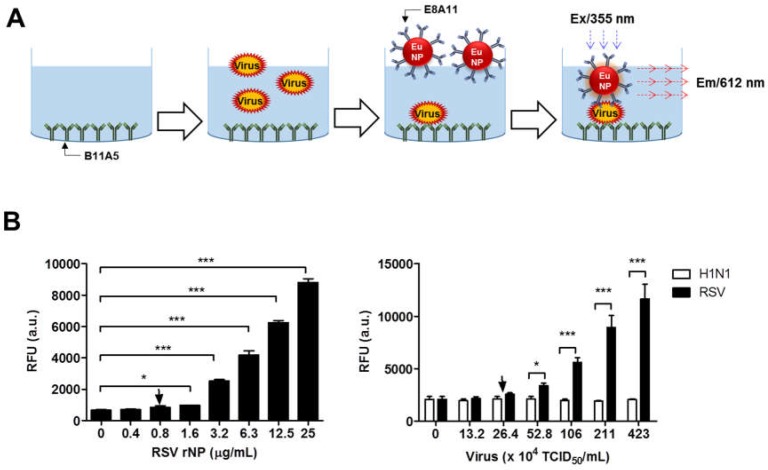
Figure 4.
Performance of sandwich fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA) using two novel monoclonal antibodies for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). (A) Sandwich FLISA using B11A5 (capture) and europium nanoparticle (Eu NP)-conjugated E8A11 (detection) was conducted with serial dilutions of RSV recombinant nucleoprotein (rNP) and virus. Fluorescence was measured for bound Eu NP-conjugated E8A11 (excitation at 355 nm and emission at 612 nm). (B) Serially diluted RSV rNP antigen, from 0.4 µg/mL to 25 µg/mL, and virus, from 13.20 × 104 to 4.23 × 106 TCID50/mL, were tested by FLISA. H1N1 was used as a negative virus control. Data (n = 3) are shown as the mean ± SD. a.u., arbitrary units; LOD, limit of detection. One-way ANOVA; * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001.