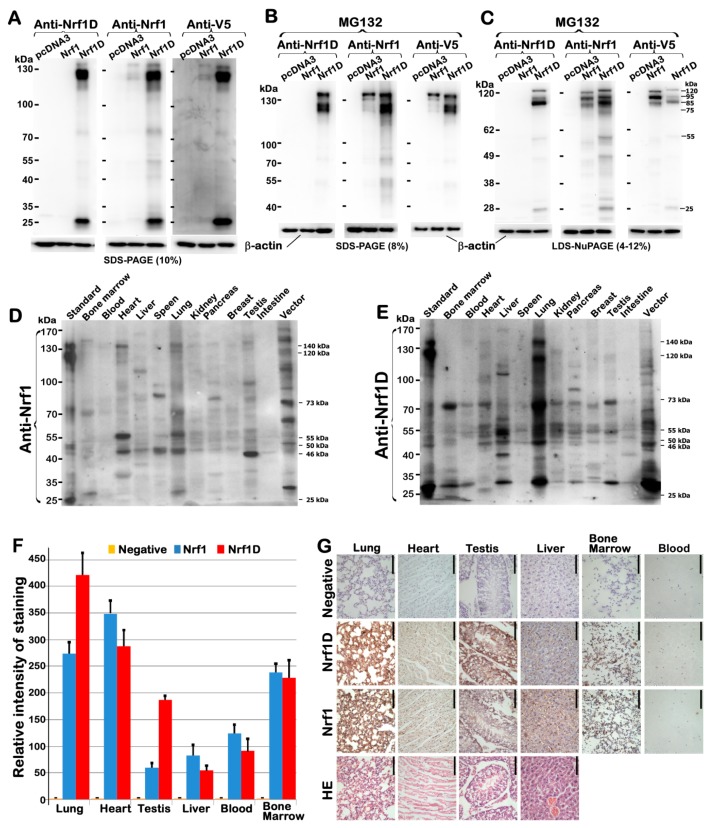
Figure 2.
Differential expression of Nrf1D and Nrf1 proteins in mouse tissues examined. (A–C) Three independent experiments of COS-1 cells, that had been transfected with an expression construct for Nrf1, Nrf1D or empty pcDNA3.1 vector and then treated with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 (5 μmol/L), showed that both Nrf1D and Nrf1 were identified by cross-immunoreactivity with three distinct antibodies against aa 192–741 in Nrf1, Nrf1D’s C-terminus-specific peptide, and their C-terminally-tagged V5 ectope, respectively. (D,E) Differential expression levels of Nrf1- and Nrf1D-derived proteins in different tissues from mice were examined by Western blotting with either Nrf1-recognized or Nrf1D-specific antibodies. (F,G) Anti-Nrf1D and -Nrf1 antibodies were also applied for immunohistochemical examinations of six different tissues, including lung, heart, testis, liver, bone marrow and blood (bar = 100 μm). Subsequently, the intensity of immunohisto- chemical staining in examined tissues was calculated and, is shown graphically (F). In addition, the first row “negative” images (G) were obtained from immunohistochemistry with the pre-immunized serum, instead of the primary antibody against Nrf1D-specific peptide, both of which was produced in the same animals.