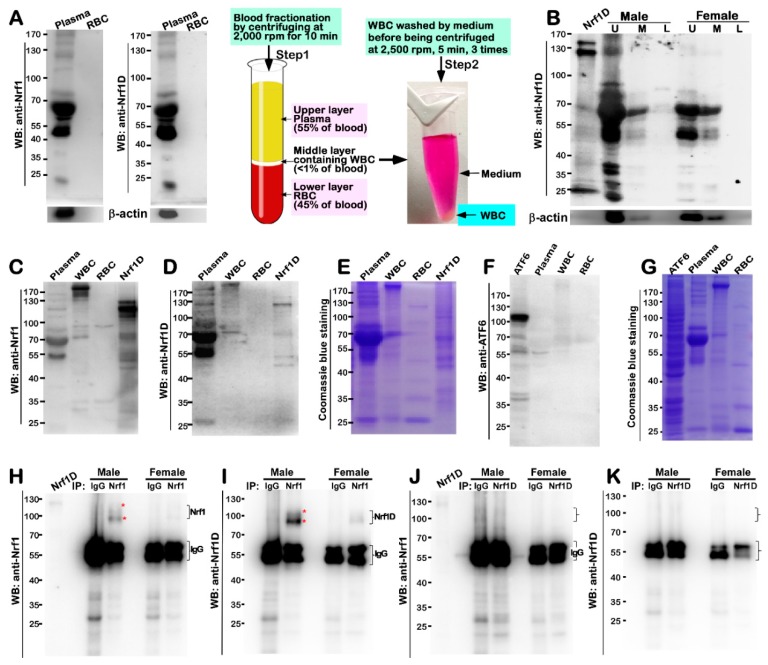
Figure 4.
Detection of Nrf1D existing in mouse blood plasma. (A) Shows immunoblots of mouse blood plasma and RBC with anti-Nrf1 and Nrf1D-specific antibodies (left upper two panels). The procedure of blood fractionation by centrifuging at different speeds was illustrated (right two panels). (B) Distinct blood fractions from male and female mice were determined by Western blotting with Nrf1D-specific peptide antibody. The Nrf1D-expressed cell lysates served as a positive control. In addition, secreted β-actin was detected in blood plasma (bottom). Abbreviations: U, upper layer of plasma; M, middle layer containing WBCs; L, lower layer containing RBCs. (C–G) Further extracts from blood plasma, RBCs and WBCs were visualized by immunoblotting with Nrf1 antibody (C) or Nrf1D-specific peptide antibodies (D). But, similar blood fractions were not cross-immunoreactive with ATF6-specific antibodies (F). Total protein extracts from the blood fractions were also seen by Coomassie Blue staining (E,G). (H–K) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of the blood plasma from male and female mice (i.e., these samples were firstly clarified by pre-incubating with pre-immunized serum and Protein-G Sepharose beads) was employed with anti-Nrf1, anti-Nrf1D antibodies, or IgG (served as an internal negative control). Subsequent immunocomplexes were visualized by Western blotting with indicated antibodies. The star (*) indicates Nrf1D isoforms from immunoprecipitation (H,I).