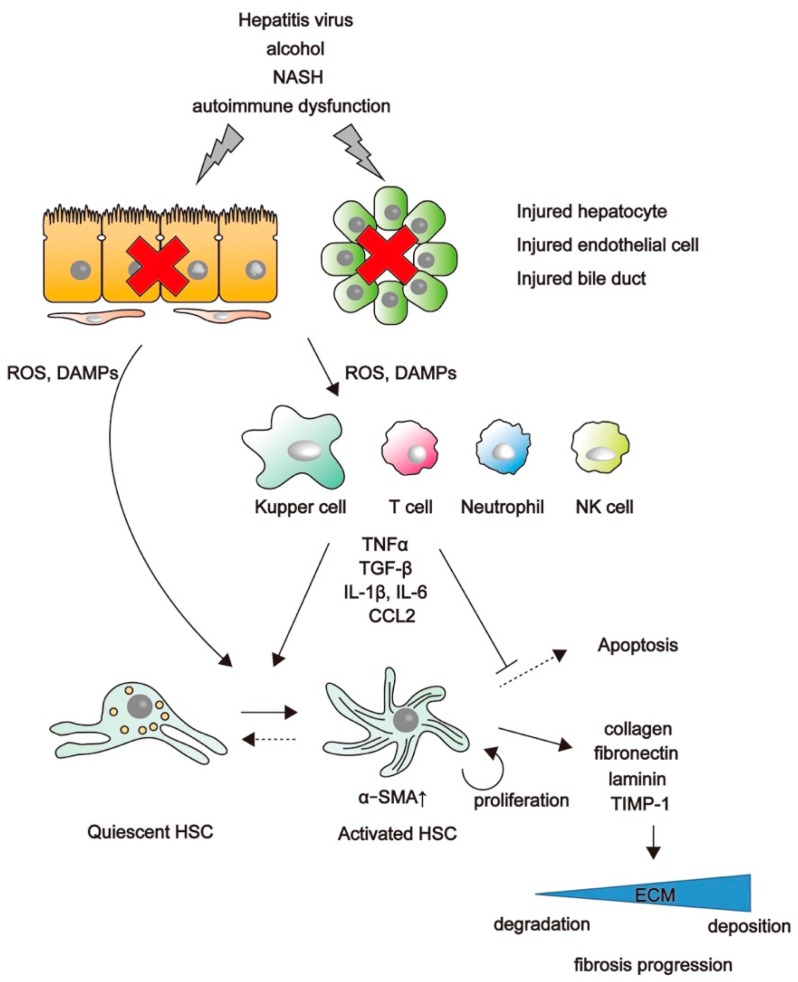
Figure 1.
Process of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and liver fibrosis progression. Damaged cells secrete damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). These factors activate quiescent HSCs directly and indirectly through the action of Kupffer cells, T cells, neutrophils, and natural killer (NK) cells. Activated HSCs produce extracellular matrix (ECM) components and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs), which accelerates the deposition of ECM components and results in liver fibrosis progression. CCL2, C–C chemokine ligand 2; IL, interleukin; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; SMA, smooth muscle actin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.