-
A, B
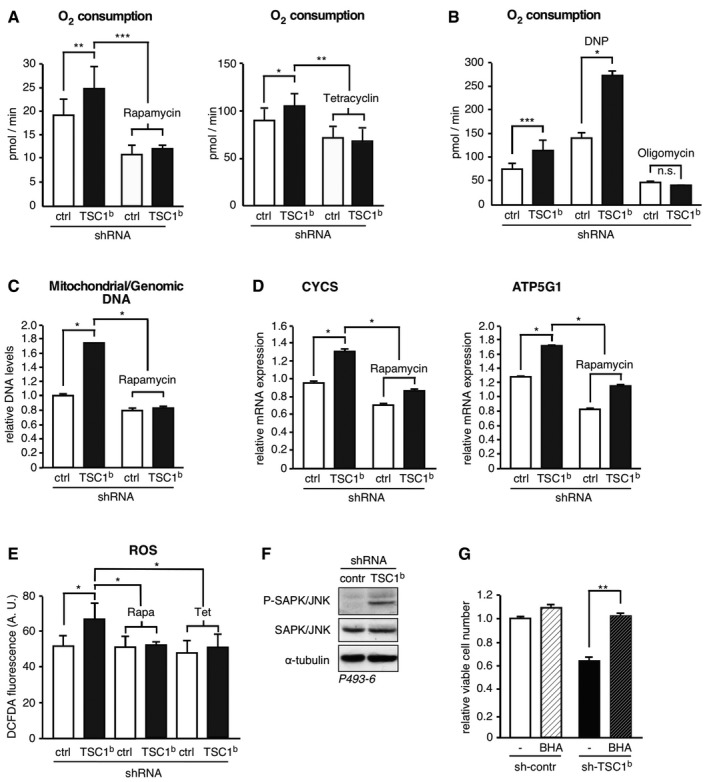
TSC1 knockdown increases respiration in an mTORC1‐ and MYC‐dependent manner. Rate of basal oxygen consumption in P493‐6 (−Tet) cells expressing scrambled control shRNA or TSC‐specific shRNA, treated with 20 nM rapamycin for 12 h, or tetracycline to repress MYC for 48 h where indicated (A) or in response to 10 μM of the chemical uncoupler DNP to determine maximal respiration or 10 μM of the ATP synthase inhibitor oligomycin where indicated (B) (mean ± SD, n = 6 biological replicates).
-
C, D
Ratio of mitochondrial to genomic DNA (C) and expression of cytochrome C (CYCS) or ATP5G1 mRNAs (D) determined by qRT–PCR in P493‐6 (−Tet) cells expressing either scrambled control shRNA or a TSC1‐specific shRNA, and treated with 20 nM rapamycin for 12 h where indicated (mean ± SD, n = 3 technical replicates).
-
E
TSC1 knockdown results in elevated ROS levels in a MYC‐ and mTORC1‐dependent manner. FACS analysis of DCF‐DA‐stained P493‐6 (−Tet) cells expressing scrambled control shRNA or a TSC1‐specific shRNA to evaluate ROS production and treated with 20 nM rapamycin for 12 h and tetracycline for 48 h where indicated (mean ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates).
-
F
TSC1 knockdown results in increased phosphorylation of SAPK/JNK. Immunoblot of SAPK/JNK Thr183/Tyr185‐phosphorylation in P493‐6 (−Tet) cells expressing scrambled control shRNA or a TSC1‐specific shRNA. α‐tubulin expression serves as loading control.
-
G
Antioxidant treatment rescues cells from death caused by TSC1 knockdown. Relative viable cell number counts of P493‐6 (−Tet) cells expressing scrambled control shRNA or TSC1‐specific shRNA 3 days after seeding equal number of viable cells (Trypan blue exclusion), in the presence of 10 μM of the antioxidant BHA where indicated (mean ± SD, n = 3 biological replicates).
‐test (two‐tailed).