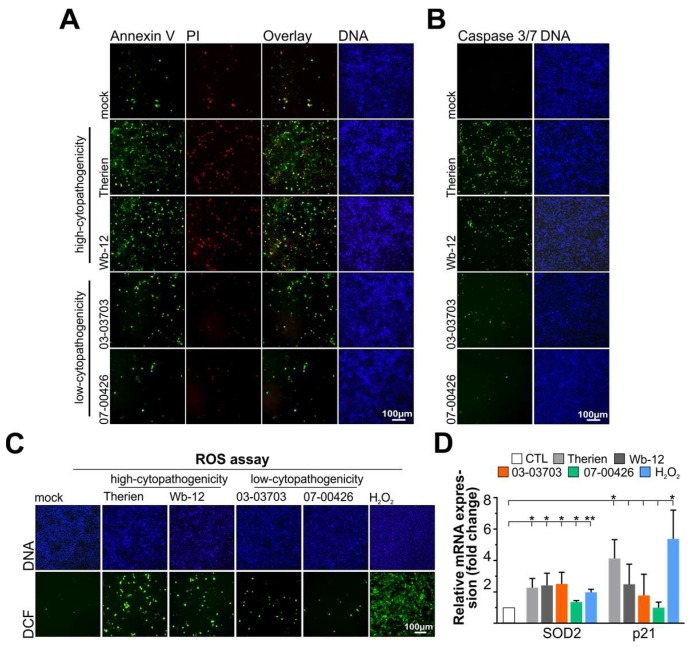
Figure 1.
Comparative analysis of the capacity of different rubella virus (RV) strains to induce apoptosis and evoke an oxidative stress response in Vero cells. (A–C) At 3 days post-infection (dpi), RV strain-specific differences in apoptosis induction were assessed through fluorescence microscopy of (A) early (Annexin V-Alexa 488-positive cells) and late (Annexin V-Alexa 488- and propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells) apoptotic response and (B) activation of caspase 3 and 7 activity through monitoring nuclear accumulation of the fluorophore after DEVD cleavage; (C) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation was monitored at 3 dpi in Vero cells infected with indicated RV strains through fluorescence microscopy of the dichlorofluorescein (DCF) fluorescence; (D) The mRNA expression level of the mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) and the oxidative stress-sensitive protein p21 was validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was used as positive control and applied for 5 h at a 1:5000 dilution. CTL, control. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.