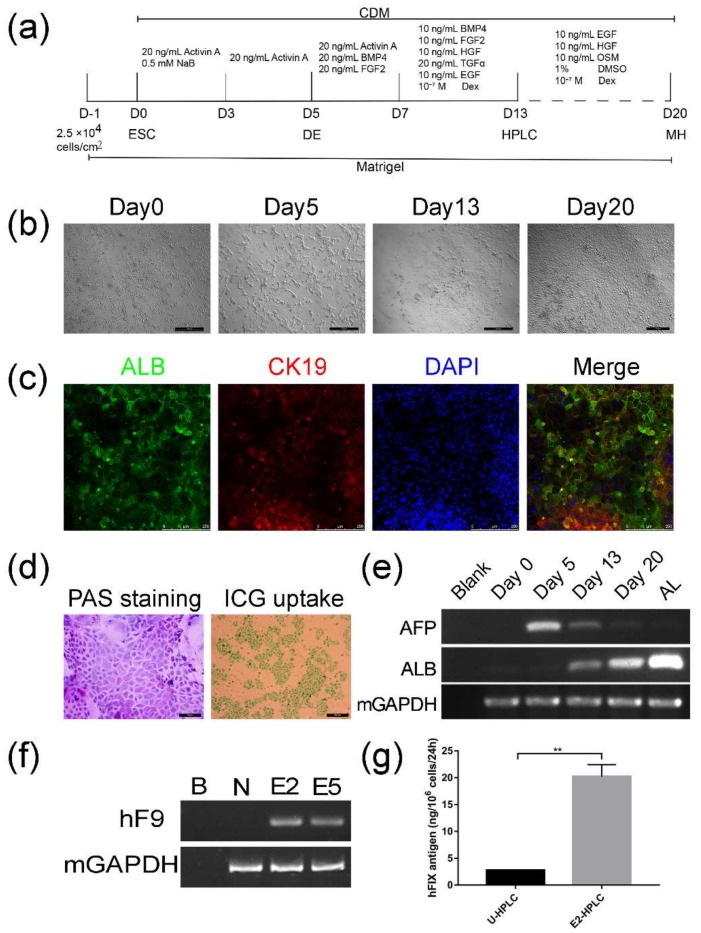
Figure 4.
Differentiation of mESCs into HPLCs and detection for exogenous FIX expression. (a) Flow chart of the modified protocol for differentiation of mESCs into HPLCs and hepatocytes. (b) Dynamic change in cellular morphology during hepatic differentiation (Day0–Day13) and hepatic maturation (Day13–Day20). Scale bar: 500 μm (Day 0, 5, 13) and 200 µm (Day 20). (c) Immunofluorescence staining of HPLCs on Day 13 with ALB (Green) and CK19 (Red). Scale bar: 250 μm (d) Periodic acid-Schiff’s (PAS) staining and indocyanine green (ICG) uptake assay for the mature hepatocyte like cells on Day 20. The purple-stained and green-stained cells indicate the ability to store glycogen and uptake ICG respectively. Scale bar: 50 μm (PAS staining) and 200 µm (ICG uptake) (e) RT-PCR showed the dynamic change of AFP and ALB mRNA during differentiation. (f) Differentiated clones on Day 13 were tested by RT-PCR for F9 transcription. B: Blank; N: untargeted mESCs as negative control. (g) Supernatant of untargeted mESCs differentiated HPLCs (U-HPLCs) and E2-HPLCs on Day 13 were gathered to examine the human FIX antigen by ELISA. DE, definitive endoderm. MH, mature hepatocyte. (**, p < 0.01).