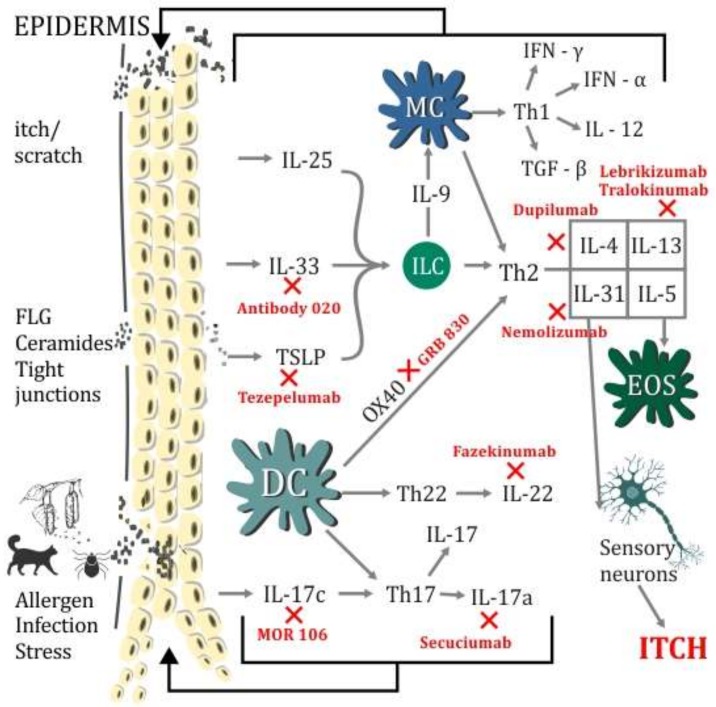
Figure 1.
Schematic summary of immunological disorders in Atopic dermatitis (AD) pathogenesis coexisting with skin barrier defect. The diagram shows inflammatory cells, Th2, Th17, and Th22-dependent inflammation in AD with cytokines, which diminish the epidermal barrier. The impact of infections, allergens, stress, and itchiness, leading to the activation of inflammatory pathways. The figure depicts the possible targets of biological agents in AD treatment. DC (dendritic cells), EOS (eosinophil), FLG (filaggrin), IL (interleukin), IFN-α (interferon-alfa), IFN-γ (interferon gamma), ILC (lymphoid cells), MC (mast cells), TGF-β (transforming growth factor beta), TSLP (thymic stromal lymphopoietin). X—indicates potential areas of new biological drugs action.