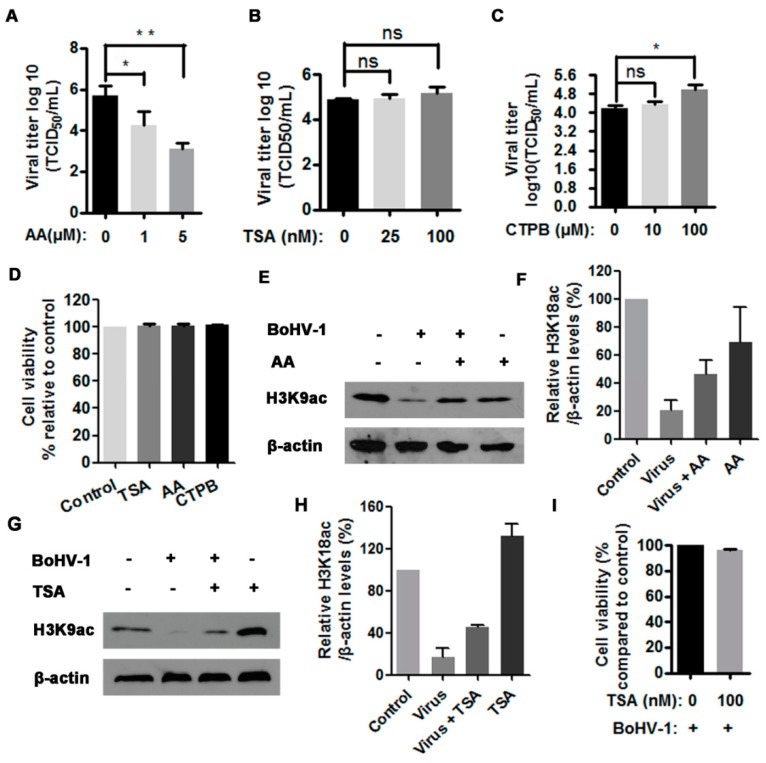
Figure 3.
The effects of HAT inhibitor on BoHV-1 productive infection. (A–C) MDBK cells in 24-wells plates were infected with BoHV-1 (MOI = 1) and treated with anacardic acid (AA) (0, 1 and 5 μM) (A), TSA (trichostatin A) (0, 50 and 100 μM) (B), CTPB [N-(4-Chloro-3-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-ethoxy-6-pentadecylbenzamide] (0, 10 and 100 μM) (C) or DMSO control for 1 h, respectively. After three washing with PBS, fresh medium with either inhibitors or DMSO control were replaced. At 24 hpi, viral yields were determined in MDBK cells. Data represent three independent experiments. Significance was assessed with the student t test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ns: not significant). (D) The cytotoxicity of AA (5 μM), TSA (100 μM), and CTPB (100 μM) was analyzed in MDBK cells with Trypan-blue exclusion test. Data represent means of three independent experiments. (E,G) MDBK cells in 60 mm dishes were uninfected or infected by BoHV-1 at an MOI of 1, along with the treatment of either AA (5 μM) (E) or TSA (100 nM) (G), or DMSO control. At 16 hpi, cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blots to detect the expression of H3K9ac. Data represent three independent experiments (+: indicated compound or virus was present, −: indicated compound or virus was not present). (I) The virus infected MDBK cells were mock treated with DMSO or TSA (100 nM) throughout infection. At 24 hpi, the cell viability was detected with Trypan-blue exclusion test. Data represent means of three independent experiments. (F,H) The band intensity was analyzed with software image J. Each analysis was compared with that of uninfected control which was arbitrarily set as 100%. The error bars denote the variability between the three independent experiments.