Table 1.
Pharmacogenetic profiles of epigenetic-based compounds currently submitted to clinical trials for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
| Drug | Compound | Pharmacogenetics | Mechanisms of action | ClinicalTrials.gov ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
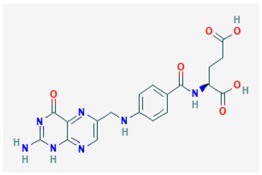
|
Name: Vitamin B9; Folic acid; Folate; 59-30-3; Folacin; Pteroylglutamic acid IUPAC name: (2S)-2-[[4-[(2-amino-4-oxo-1H-pteridin-6-yl)methylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid Molecular formula: C19H19N7O6 Molecular Weight: 441.40 g/mol Category: SAMe methyl donors Targets: SAMe |
Pathogenic genes: ADORA2A, AOX1, APOB, CDKN2A, COMPT Mechanistic genes: ALDH1A1, GSTA1, GSTP1, IL2, IL6, NAT2, SOD3, TNF, VGFA Metabolic genes: Substrate:ABCG2, MTHFR Inhibitor:ABCB1, ERCC2, MTHFR Inducer:CYP2C9 Transporter genes: ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC3, SLC19A1, SLC22A8, SLC28A2, SLCOB1 Pleiotropic genes: PPAR, TNF, TP53, VCAM1 |
|
NCT00056225-Phase III NCT01320527-Phase II NCT02457507-Phase IV |
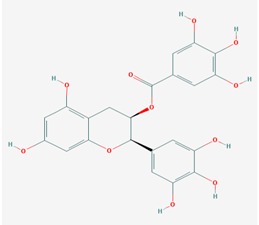
|
Name: EGCG, (−)-epigallocatechin gallate, epigallocatechin 3-gallate, tea catechin, teavigo, catechin deriv., 989-51-5 IUPAC name: [(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate Molecular formula: C22H18O11 Molecular Weight: 458.37 g/mol Category: DNMT inhibitors Targets: DNMT1 |
Pathogenic genes: APP, BACE1, CDX2, EGFR, FAS PIK3CA, ROS1 Mechanistic genes: APP, BACE1, BMP2, CDX2, CHRNA7, ECEs, EGFR, IRS1, PIK3CA, ROS1 Metabolic genes: Inhibitor:SOD Transporter genes: CD36, SLC5A1, SLC27A4, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3 Pleiotropic genes: ACACA, CHRNA7, SCD |
|
NTC00951834-Phases II, III |
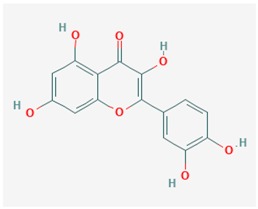
|
Name: Quercetin; Sophoretin; Quercetol; Meletin; Xanthaurine; Quercitin; 3,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone IUPAC name: 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one Molecular formula: C15H10O7 Molecular Weight: 302.24 g/mol Category: DNMT inhibitors Targets: DNMT1 |
Pathogenic genes: IL1R, NFkB, Ccl8, IKK, STAT3, CD4, CDK2, IL2 Mechanistic genes: MTND4, CDKN2A, PRDX4, DIO2, HSD17B1, MSH2, GSS, COMT, FOS, CRP, NR1I3, PON1 Metabolic genes: Substrate:UGT1A1, UGT1A3, GSTT1, CYP2J2, GSTK1, CYP2C8, CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1, GSTA1, CYP19A1 Inhibitor:SULT1E1 Transporter genes: ABCB1, ABCG2 |
|
NCT01716637-Phase I |
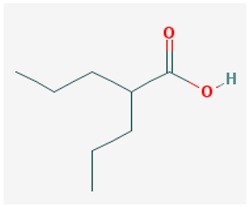
|
Name: Valproic acid, 2-propylpentanoic acid, depakene, depakine, ergenyl, dipropylacetic acid, mylproin, convulex, myproic acid IUPAC name: 2-propylpentanoic acid Molecular formula: C8H16O2 Molecular Weight: 144.21 g/mol Category: HDAC inhibitors Targets: Class I HDAC; Class II HDAC |
Pathogenic genes: CREB1, IL6, LEP, SCN2A, TGFB1, TNF, TRNK Mechanistic genes: ABAT, CDK5, GSK3B, HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8, HDAC9, LEP, LEPR, SCNs, SMN2 Metabolic genes: Substrate:CYP2A6 (major), CYP2C9 (major), CYP4B1 (major), CYP1A1 (minor), CYP2B6 (minor), CYP2C19 (minor), CYP2E1 (minor), CYP3A4 (minor), CYP4F2 (minor), ABCB1 (minor), UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A8, UGT1A10, UGT2B7 Inhibitor: ABCB1, ACADSB, AKR1A1, CYP2C9 (strong), CYP2A6 (moderate), CYP2C19 (moderate), CYP3A4 (moderate), CYP2D6 (weak), HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8, HDAC9, UGT1A9, UGT2B1, UGT2B7 Inducer: ABCB1, AKR1C4, CASR, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP3A4, CYP7A1, MAOA, NR1I2, SLC5A5, SLC6A2, SLC12A3, SLC22A16 Transporter genes: ABCB1, ABCC2, ABCG1, ABCG2, SCNs, SLC5A5, SLC6A2, SLC12A3, SLC22A16 Pleiotropic genes: ABL2, AGPAT2, ASL, ASS1, CDK4, CHRNA1, COL1A1, CPS1, CPT1A, DRD4, FMR1, FOS, HBB, HFE, HLA-A, HLA-B, ICAM1, IFNG, IL6, IL10, LEPR, NAGS, NR3C1, OTC, PTGES, STAT3, TGFB1, TNF, TP53 |
|
NTC01729598-Phase I NTC00088387-Phase II NTC00071721-Phase III |
|
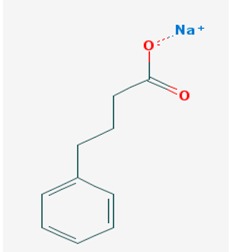
Name: sodium phenylbutyrate, buphenyl, 4-phenylbutiric acid, 4-phenylbutonoic acid, benzenebutanoic acid, benzenebutyric acid, butyric acid IUPAC name: sodium;4-phenylbutanoate Molecular formula: C10H11NaO2 Molecular Weight: 186.182909 g/mol Category: HDAC inhibitors Targets: Class I HDAC, Class IIa HDAC, Class IIb HDAC |
Pathogenic genes: ARG1, ASS1, BCL2, CPS1, NAGS, OTC Mechanistic genes: BCL2, BDNF, EDN1, HDACs, HSPA8, ICAM1, NFKB2, NT3, VCAM1 Metabolic genes: Inhibitor:HDACs Inducer:ARG1, CFTR, CYP2B6, NFKB2 Transporter genes: CFTR Pleiotropic genes: ASL, BDNF, VCAM1 |
|
NCT03533257-Phase II NCT02046434-Phase I |
|
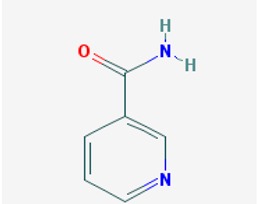
Name: Nicotinamide, niacinamide, vitamin PP, aminicotin, nicotinic acid amide, amixicotyn, 3-pyridinecarboxamide, papulex, nicotylamide IUPAC name: pyridine-3-carboxamide Molecular formula: C6H6N2O Molecular Weight: 122.12 g/mol Category: SIRT inhibitors Targets: class III HDAC (SIRT1-7) |
Pathogenic genes: IL6, IL8, PTGS2, TNF Mechanistic genes: ARTs, CAT, CLOCK, FOXO3, GPXs, IL6, IL8, PARP1, PTGS2, SIRT1, SOD1, TNF Metabolic genes: Inhibitor:CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP2E1, SIRT1-7 Pleiotropic genes: CAT, PARP1 |
|
NTC00580931-Phases I, II NTC03061474-Phase II |
|
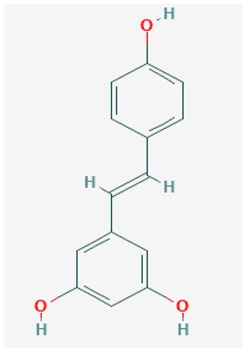
Name: Resveratrol, trans-resveratrol, 501-36-0, 3,4′,5-trihydroxystilbene, (E)-resveratrol, resvida IUPAC name: 5-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]benzene-1,3-diol Molecular formula: C14H12O3 Molecular Weight: 228.24 g/mol Category: SIRT inhibitors Targets: class III HDAC (SIRT1) |
Pathogenic genes: BCL2, CAV1, ESR1, ESR2, GRIN2B, NOS3, PTGS2, TNFRSF10A, TNFRSF10B Mechanistic genes: APP, ATF3, BAX, BAK1, BBC3, BCL2, BCL2L1, BCL2L11, BIRC5, CASP3, CAV1, CFTR, ESR1, ESR2, GRIN1, GRIN2B, HTR3A, NFKB1, NOS3, PMAIP1, PTGS1, PTGS2, SIRT1, SIRT3, SIRT5, SRC, TNFRSF10A, TNFRSF10B, TRPs Metabolic genes: Substrate:CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP1B1, CYP2E1, GSTP1, PTGS1, PTGS2 Inhibitor:CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, NQO2 Inducer:CYP1A2, SIRT1 Transporter genes: ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCC4, ABCC8, ABCG1, ABCG2, CFTR, TRPs |
|
NCT01504854-Phase II NCT00678431-Phase III NCT00743743-withdrown NCT02502253-Phase I |
|
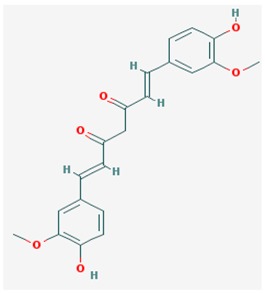
Name: Curcumin, diferuloylmethane, turmeric yellow, turmeric, gelbwurz, kacha haldi, curcuma, haldar, souchet IUPAC name: (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione Molecular formula: C21H20O6 Molecular Weight: 368.38 g/mol Category: HAT inhibitors Targets: HATs |
Pathogenic genes: BACE1, CCND1, CDH1, GSK3B, IL1A, IL6, JUN, MSR1, PSEN1, PTGS2, SNCA, SREBF1, TNF Mechanistic genes: AKT1, PRKAs, BACE1, CCND1, CDH1, CDKs, CRM1, CTNNB1, EGF, GSK3B, HDACs, HIF1A, IL1A, IL6, JUN, MMPs, MSR1, NFKB1, NOS2, PDGFRs, PSEN1, PTGS2, SNCA, SOCS1, SOCS3, SREBF1, STAT3, TNF, VEGFA Metabolic genes: Inhibitor:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, EP300 Inducer:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4 Transporter genes: ABCA1, SNCA Pleiotropic genes: CTNNB1, MSR1 |
|
NTC00164749-Phases I, II NTC00099710-Phase II NTC01716637-Phase I NTC01811381-Recruting NTC02114372-Recruting |
|
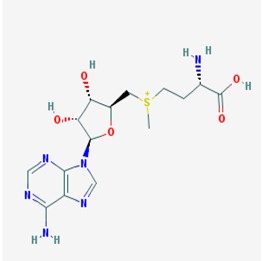
Name: S-adenosylmethionine, ademetionine, AdoMet, donamet, methioninyladenylate, S-adenosyl-l-methionine, SAM-e IUPAC name: [(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl]-[[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl]-methylsulfanium Molecular formula: C15H23N6O5S+ Molecular Weight: 399.45 g/mol Category: HMT inhibitors Targets: HMTs |
Pathogenic genes: AKT, ERK, GNMT, MAT1A, PSEN1 Mechanistic genes: AMD1, CAT, CBS, GCLC, GNMT, GSS, NOS2, ROS1, STAT1, TNF Metabolic genes: Substrate:COMT, GNMT, TPMT, SRM Inhibitor:ABCB1, CYP2E1, NOS2 Transporter genes: SLC25A26 Pleiotropic genes: CAT, TNF |
|
NTC01320527-Phase II NTC00070941-Phases II, III |
ABAT: 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase; ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily A, member 1; ABCB1: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B, member 1; ABCC1: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 1; ABCC2: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 2; ABCC3: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 3; ABCC4: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 4; ABCC8: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily C, member 8; ABCG1: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily G, member 1; ABCG2: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily G, member 2; ABL2: c-abl proto-oncogene 2, non-receptor tyrosine kinase; ACACA: acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha; ACADSB: acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, short/branched chain; ADORA2A: adenosine 2A2 receptor; AGPAT2: 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 2; AKR1A1: aldo-keto reductase family 1 member A1; AKT1: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; ALDH1A1: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A1; AMD1: adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1; AOX1: aldehyde oxidase 1; APOB: apolipoprotein B; APP: amyloid beta precursor protein; ARG1: arginase 1; ARTS: ADP ribosyltransferases; ASL: argininosuccinate lyase; ASS1: argininosuccinate synthase 1; ATF3: activating transcription factor 3; BACE1: beta-secretase 1; BAK1: BCL2 antagonist/killer 1; BAX: BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator; BBC3: BCL2 binding component 3; BCL2: B-cell lymphoma 2, apoptosis regulator; BCL2L1: BCL2 like 1; BCL2L11: BCL2 like 11; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BIRC5: baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5; BMP2: bone morphogenetic protein 2; CASP3: caspase 3; CASR: calcium sensing receptor; CAT: catalase; CAV1: caveolin 1; CBS: cystathionine-beta-synthase; Ccl8: C-C motif chemokine ligand 8; CCND1: cyclin D1; CD36: CD36 molecule; CD4: CD4 molecule; CDH1: cadherin 1; CDK: cyclin-dependent kinase; CDK2: cyclin-dependent kinase 2; CDK4: cyclin-dependent kinase 4; CDK5: cyclin-dependent kinase 5; CDKN2A: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; CDX2: caudal type homeobox 2; CFTR: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; CHRNA1: cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 1 subunit; CHRNA7: cholinergic receptor nicotinic alpha 7 subunit; CLOCK: circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; COL1A1: collagen type I alpha 1 chain; COMT: catechol-O-methyltransferase; CPS1: carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1; CPT1A: carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; CREB1: cAMP responsive element binding protein 1; CRM1: exportin CRM1; CRP: C-reactive protein; CTNNB1: catenin beta 1; CYP19A1: cytochrome P450 family 19 subfamily A member 1; CYP1A1: cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 1; CYP1A2: cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 2; CYP1B1: cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily B member 1; CYP2A6: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily A member 6; CYP2B6: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily B member 6; CYP2C19: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 19; CYP2C8: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 8; CYP2C9: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9; CYP2D6: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily D member 6; CYP2E1: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily E member 1; CYP2J2: cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily J member 2; CYP3A4: cytochrome P450 family 3 subfamily A member 4; CYP4B1: cytochrome P450 family 4 subfamily B member 1; CYP4F2: cytochrome P450 family 4 subfamily F member 2; CYP7A1: cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1; DIO2: iodothyronine deiodinase 2; DR4: drought-repressed 4; ECEs: endothelin converting enzymes; EDN1: endothelin 1; EGF: epidermal growth factor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; EP300: E1A binding protein p300; ERCC2: excision repair, complementing defective, in Chinese hamster, 2; ERK: extracellular regulated MAP kinase; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; ESR2: estrogen receptor 1; FAS: Fas (TNF receptor superfamily member 6); FMR1: fragile X mental retardation 1; FOS: FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene; FOXO3: forkhead box O3; GCLC: glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit; GNMT: glycine N-methyltransferase; GPX: phage tail protein; GRIN1: glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 1; GRIN2B: glutamate ionotropic receptor NMDA type subunit 2B; GSK3B: glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; GSS: glutathione synthetase; GSTA1: glutathione S-transferase alpha 1; GSTK1: glutathione S-transferase kappa 1; GSTP1: glutathione S-transferase pi 1; GSTT1: glutathione S-transferase theta 1; HATs: Histone acetyltransferases; HBB: hemoglobin subunit beta; HDACs: histone deacetylases; HDAC 1-9: histone deacetylases 1–9; HFE: hemochromatosis; HIF1A: hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit; HLA-A: major histocompatibility complex, class I, A; HLA-B: major histocompatibility complex, class I, B; HMTs: Histone Methyl Transferases; HSD17B1: hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 1; HSPA8: heat-shock 70-KD protein 8; HTR3A: 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3A; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IFNG: interferon gamma; IKK: I-kappaB kinase beta; IL10: interleukin 10; IL1A: interleukin 1A; IL1R: interleukin receptor; IL2: interleukin 2; IL6: interleukin 6; IL8: interleukin 8; IRS1: insulin receptor substrate 1; JUN: Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit; LEP: leptin; LEPR: leptin receptor; MAOA: monoamine oxidase A; MAT1A: methionine adenosyltransferase 1A; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; MSH2: mutS homolog 2; MSR1: macrophage scavenger receptor 1; MTHF: 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate; MTHFR: 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate receptor; MTND4: mitochondrially encoded NADH dehydrogenase 4; NAGS: N-acetylglutamate synthase; NAT2: N-actyltransferase 2; NFkB: nuclear factor kappa-B; NFkB1: nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1; NFkB2: nuclear factor kappa B subunit 2; NOS2: nitric oxide synthase 2; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; NQO2: N-ribosyldihydronicotinamide:quinone reductase 2; NR1I2: nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 2; NR1I3: nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 3; NR3C1: nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1; NT3: neurotrophin 3; OTC: ornithine carbamoyltransferase; PARP1: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; PDGFR: platelet derived growth factor receptor; PIK3CA: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PMAIP1: phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1; PON1: paraoxonase 1; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PRDX4: peroxiredoxin 4; PRKA: serine protein kinase PrkA; PSEN1: presenilin 1; PTGS1: prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1; PTGS2: prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2; ROS1: ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase; SAMe: S-adenosylmethionine; SCD: stearoyl-CoA desaturase; SCN2A: sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 2; SIRT1-7: sirtuins 1–7; SLC12A3: solute carrier family 12 member 3; SLC22A16: solute carrier family 22 member 16; SLC25A26: solute carrier family 25 member 26; SLC27A4: solute carrier family 27 member 4; SLC5A1: solute carrier family 5 member 1; SLC5A5: solute carrier family 5 member 5; SLC6A2: solute carrier family 6 member 2; SLC19A1: solute carrier family 19 member 1; SLC22A8: solute carrier family 22 member 8; SLC28A2: solute carrier family 28 member 8; SLCO1B1: solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1; SLCO1B3: solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B3; SMN2: survival of motor neuron 2, centromeric; SNCA: synuclein alpha; SOCS1: suppressor of cytokine signaling 1; SOCS3: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; SOD1: superoxide dismutase 1; SOD3: superoxide dismutase 3; SRC: SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase; SREBF1: sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1; SRM: spermidine synthase; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; SULT1E1: sulfotransferase family 1E member 1; TGFB1: transforming growth factor beta 1; THF: Tetrahydrofolate; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF10A: TNF receptor superfamily member 10A; TNFRSF10B: TNF receptor superfamily member 10B; TP53: tumor protein p53; TPMT: thiopurine S-methyltransferase; TRNK: mitochondrially encoded tRNA lysine; UGT1A1: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A1; UGT1A10: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A10; UGT1A3: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A3; UGT1A4: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A4; UGT1A6: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A6; UGT1A8: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A8; UGT1A9: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 1 member A9; UGT2B1: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member B1; UGT2B7: UDP glucuronosyltransferase family 2 member B7; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor A.
