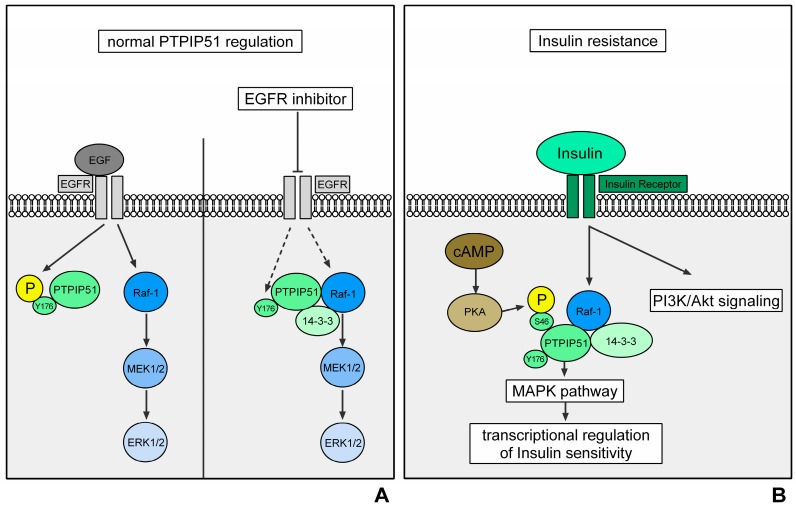
Figure 1.
Regulation of PTPIP51 interactions in normal cells (represented by the HaCat cell line). Activation of the EGFR via the binding of EGF induces an activation of Raf-1 via several signaling molecules. Raf-1 depicts the MAPKKK of the ERK signaling. Its activation triggers a signaling cascade via MEK1/2 and ERK1/2, which ultimately initiates transcription. The EGFR also phosphorylates the Tyr176 residue of PTPIP51 and thereby inhibits its interaction with Raf-1. This mechanism prevents an overshooting activation of the MAPK pathway. The right side of the figure represents the interactions when EGFR is inhibited. The inhibition of EGFR leads to an omission of Tyr176 phosphorylation of PTPIP51 via the EGFR. The dephosphorylation of PTPIP51 at Tyr176 induces the formation of the Raf-1/14-3-3β/PTPIP51 complex and thus a stimulation of the MAPK pathway. This mechanism partially compensates for the EGFR inhibition (black arrows indicate a phosphorylation/activation; dotted black arrows indicate a reduced phosphorylation/activation) (A); regulation of PTPIP51 interactions in insulin resistance. Activation of the insulin receptor induces the activation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling and the MAPK pathway, especially the ERK signaling. Here, PTPIP51 stimulates the signaling on Raf-1 level and potentially modulates the insulin sensitivity on transcriptional level. Protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylates the Ser46 residue of PTPIP51 and thereby stimulates the binding of PTPIP51 and Raf-1 via 14-3-3β (black arrows indicate a phosphorylation/activation) (B).