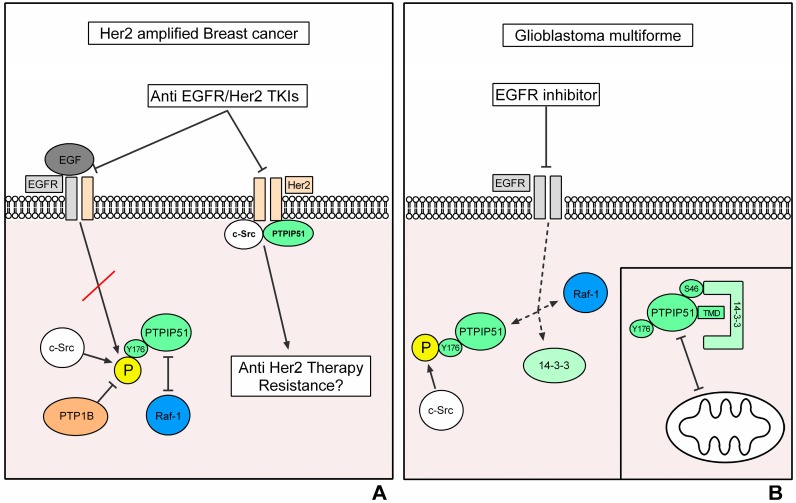
Figure 2.
Regulation of PTPIP51 interactions in breast cancer. The inhibition of EGFR in Her2 amplified breast cancer cells induces the same effects as observed in the HaCat cell line upon EGFR inhibition regarding the formation of the Raf-1/14-3-3β/PTPIP51 complex. The sensitivity of Her2 amplified breast cancer cells towards EGFR-targeted TKIs correlates with the regulation of the interaction of PTPIP51 with c-Src. The selective inhibition of Her2 induces a formation of a PTPIP51/Her2/c-Src complex, which depicts a potential resistance mechanism against anti-Her2 therapies (black arrows indicate a phosphorylation/activation, arrows with vertical bar as arrow head indicate an inhibition of interaction/activation) (A); regulation of PTPIP51 interactions in Glioblastoma multiforme. The left side of the figures depicts the regulation of PTPIP51 interactome under EGFR inhibition. Contrary to the expectations, the inhibition of the EGFR induces a disruption of the Raf-1/14-3-3β/PTPIP51 complex. The right side of the figure shows that the upregulated 14-3-3 protein levels in gliomas of high malignancy potentially inhibit the translocation of PTPIP51 to the mitochondrion and thus its apoptosis-inducing effects (black arrows indicate a phosphorylation/activation, arrows with vertical bar as arrow head indicate an inhibition of interaction/activation, dotted black arrows indicate a dissolution of the Raf-1/14-3-3β/PTPIP51 complex via EGFR inhibition) (B).