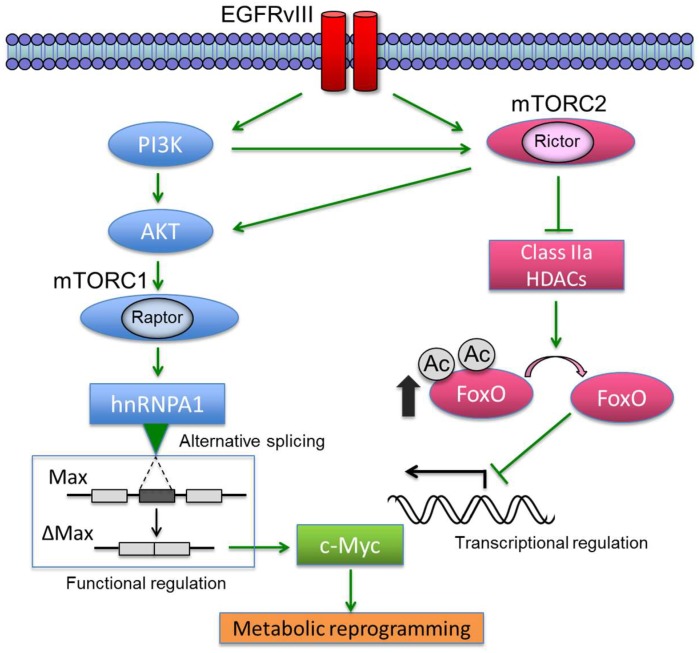
Figure 1.
EGFRvIII controls c-Myc through two interlacing and synergistic mechanisms. EGFRvIII-mTORC1 signaling promotes glycolytic metabolism by activating hnRNPA1-dependent alternative splicing of a Myc-binding partner Delta Max, thereby functionally augmenting the oncogenic activity of c-Myc. Alternatively, EGFR-mTORC2 signaling controls c-Myc transcription, translation and protein level through FoxO acetylation, resulting in the enhancement of metabolic reprogramming. These findings point to the central role of c-Myc in regulating EGFRvIII-activated glycolytic metabolism. EGFRvIII: epidermal growth factor receptor variant III; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; mTORC1/2: mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1/2; HDAC: histone deacetylase; hnRNPA1: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1; Max: myc-associated factor X; FoxO: forkhead box O; Ac: acetyl-group.