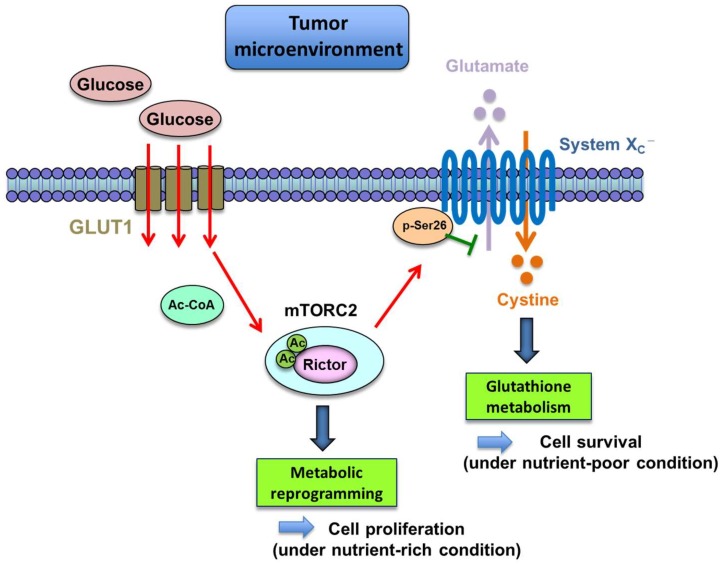
Figure 3.
The function of mTORC2 as a sensor of glucose and amino acid. mTORC2 is activated by glucose through acetylation of Rictor, playing a role as a sensor of glucose. Phosphorylation of Ser26 of xCT by mTORC2 represses its function as glutamate-cystine anti-transporter. Under nutrient (glucose) poor conditions, lower mTORC2 signaling could tilt the balance from proliferation to survival by favoring glutamate efflux, cystine uptake, and glutathione synthesis to protect tumor cells from cellular stress.