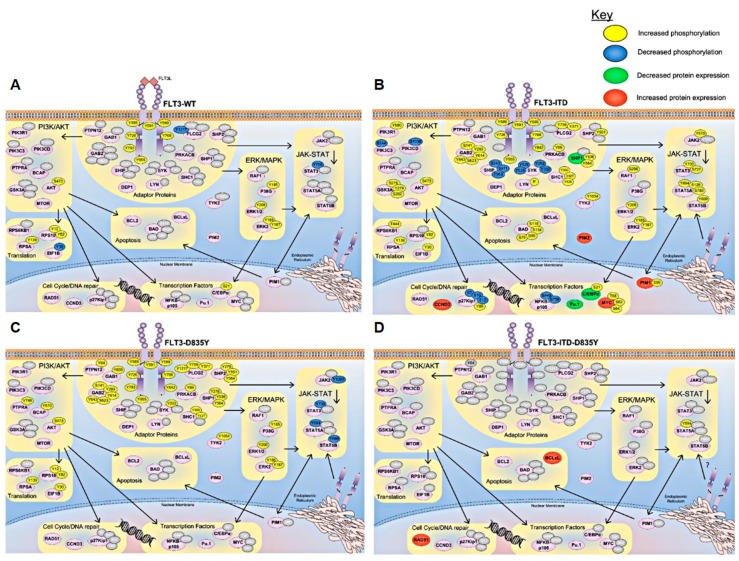
Figure 2.
Canonical FLT3 and mutant FLT3 signaling pathways. Similar and divergent signaling pathways of wild-type and mutant FLT3 identified by functional genomic studies and large scale proteomic profiling experiments. (A) Upon binding of the FLT3 ligand (FLT3L), the FLT3 receptor undergoes a change in conformation and trans-autophosphorylation. (B) FLT3-ITD, (C) FLT3-TKD and (D) FLT3-ITD-TKD dual mutations lead to constitutive, ligand independent activation of the FLT3 receptor. Subsequent recruitment of adaptor proteins effects the activation of downstream kinase signaling pathways, such as MAPK, JAK-STAT, and PI3K. Coloring indicates activation of pathway phosphorylation or expression changes associated with the wild-type and mutant FLT3 receptor forms. Numbers indicate amino acid residues of the human protein sequence. Figure created using data from references [18,72,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110].