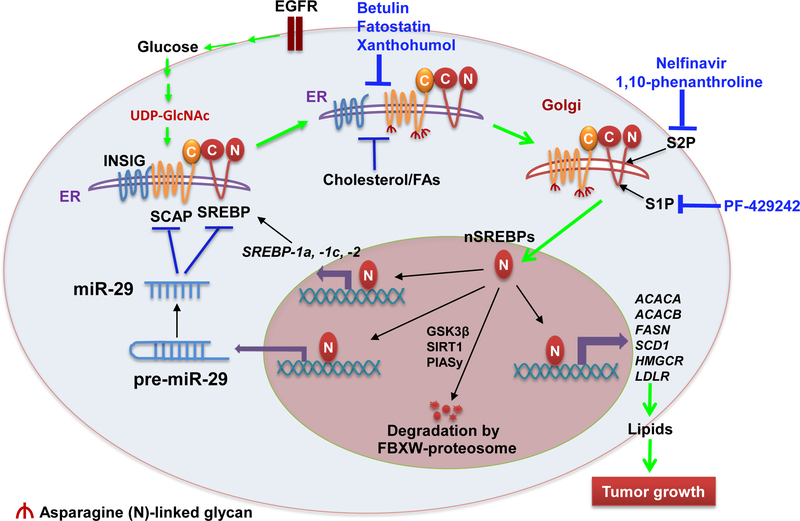
Figure 1.
Regulation of SCAP/SREBP activation in Cancer Cells.
In cancer cells, oncogenic EGFR signaling increases glucose uptake and enhances the synthesis of UDPGlcNAc, the end-product of the hexosamine synthesis pathway, promoting the N-glycosylation of SCAP, which enables SCAP dissociation from INSIG and leads to SCAP/SREBP trafficking from the ER to the Golgi. In the Golgi, SREBPs are sequentially cleaved by S1P and S2P proteases to release their NH2-terminal forms, which enter into the nucleus to activate the expression of key lipogenic genes, including themselves, forming a feedforward loop to activate lipid metabolism. Moreover, the newly synthesized INSIG1, cholesterol and unsaturated fatty acids mediated by SREBPs enhance the binding of INSIG and SCAP to retain SCAP/SREBP complex in the ER, forming a negative feedback loop to regulate SREBP activation. In addition, the nuclear SREBP forms are degraded by ubiquitin E3 ligase FBXW-mediated proteasome system, a process regulated by phosphorylation, acetylation and sumoylation by GSK3β, SIRT1 and PIAsy, respectively. Recently, miR-29 was found to be transcriptionally upregulated by SREBP-1, and in turn to inhibit SCAP and SREBP expression, mediating an additional negative feedback loop controlling this signaling pathway. Various inhibitors shown in blue, which inhibit SREBP translocation or maturation, have been tested in cancer cells and have shown promising anti-tumor effects. Abbreviation: ACACA, acetyl-coA carboxylase alpha; ACACB, acetyl-coA carboxylase beta; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FAs, fatty acids; FASN, fatty acid synthase; FBXW, F-box and WD repeat domain containing; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; HMGCR, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase; INSIG, insulin-induced gene proteins; LDLR, low density lipoprotein receptor; PIASy, STAT Y; S1P, site-1 protease; S2P, site-2 protease; SCAP, SREBP cleavage-activating protein; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; SREBP, Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; nSREBPs, nuclear forms of SREBPs.