Figure 4.
Identification of IκBα-pY42 as a novel site recognized by PTPL1.
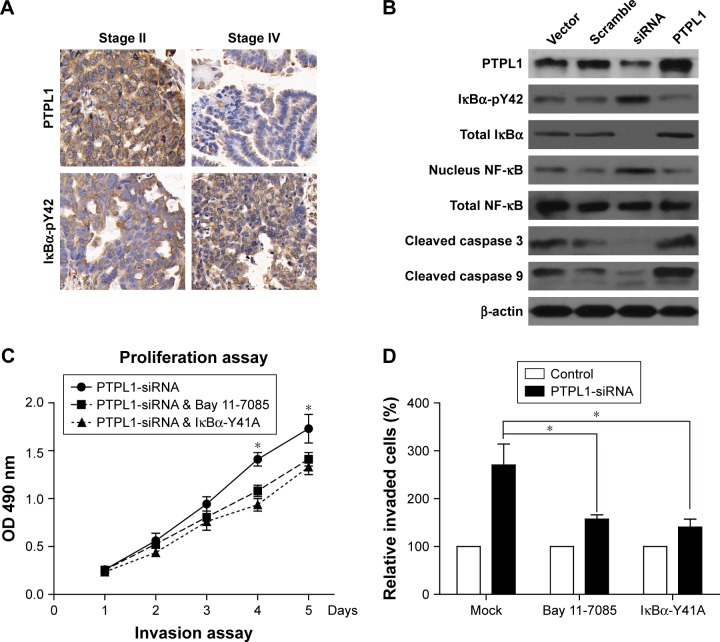
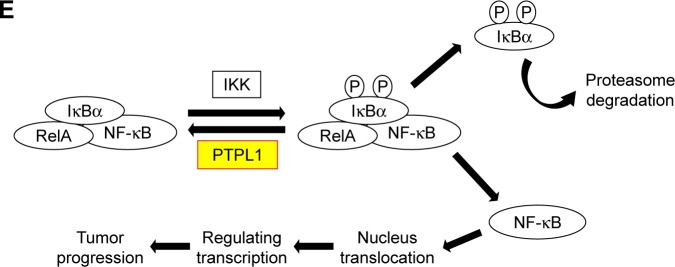
Notes: (A) Both PTPL1 and IκBα were predominantly localized in the cytoplasm. Importantly, IκBα-Y42 phosphorylation level was negatively correlated with the PTPL1 level. (B) In OV-90 cells transfected with PTPL1 plasmids, the phosphorylation on IκBα-Y42 was lower than that in control cells, which was consistent with the data from clinical samples. Subsequently, the phosphorylated IκBα protein underwent degradation, thereby released the NF-κB into the cell nucleus, as reflected by Western blot. By conducting the proliferation (C) and invasion (D) experiments, we found that the tumor-promoting effects of PTPL1-silencing were attenuated by IκBα inhibitor Bay 11-7085 or its tyrosine-alanine (Y42A) mutation. (E) The signaling axis of PTPL1-IκBα-pY42-NF-κB is shown in a schematic model. *p<0.05.
Abbreviation: PTPL1, protein tyrosine phosphatase L1.