Figure 4.
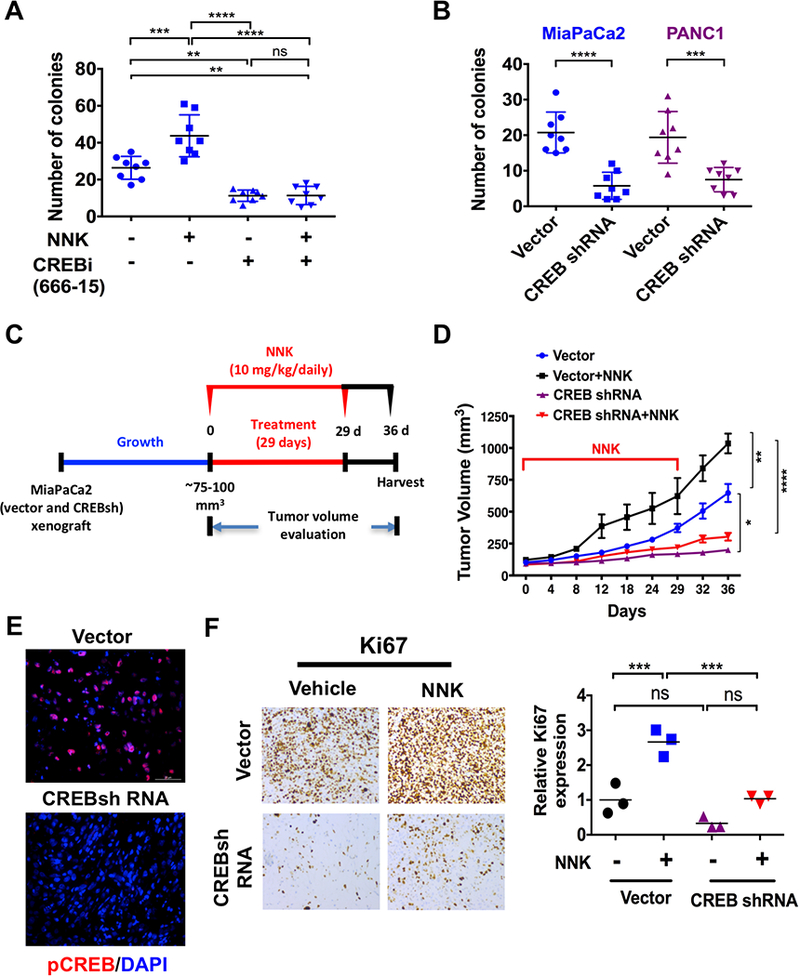
CREB inhibition (CREBi) effectively suppresses NNK-induced pancreatic tumor growth. A. MiaPaCa2 cells were treated with NNK (1 μmol/L) and/or CREB inhibitor (1 μmol/L) and analyzed for number of colonies. Colony size results were calculated from eight photographs analyzed from triplicate wells. Data are represented as mean ± S.D. B. MiaPaCa2 and PANC1 CREB shRNA cells were analyzed for number of colonies. Colony size results were calculated from eight photographs analyzed from triplicate wells. C. Experimental design for NNK treatment in CREBsh MiaPaCa2 xenograft mouse model (n=5 per experimental cohort). D. CREBsh MiaPaCa2 and empty vector cells were subcutaneously injected onto the flank of Fox1-nu/nu mice and treated with NNK at 10 mg/100g by intraperitoneal administration, three times/week for 29 days. Tumor volumes were measured up to 36 days. The tumors were later dissected and growth curves were measured and represented as mean ± S.D (n=5). E. Immunofluorescence staining of pCREB expression in vehicle or NNK-treated vector and CREBsh MiaPaCa2 flank xenografts. F. Representative Ki67 staining of vehicle or NNK-treated vector and CREBsh MiaPaCa2 flank xenograft tissues (left panel). Quantification of Ki67 staining data obtained from vehicle or NNK-treated vector and CREBsh MiaPaCa2 flank xenografts (right panel) (n=3; ns, P > 0.05; ***, P < 0.001, Student t test). ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.
