Figure 4 |. The stabilizing mechanism of the extended αv-integrin.
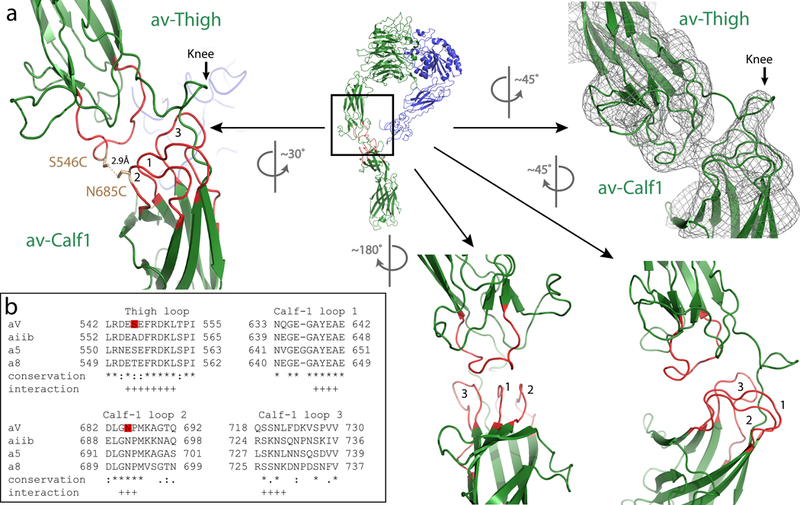
a, Ribbon model of the αvβ8 ectodomain subclass (i), en face, from Fig. 2 with the knee region indicated by a box. The corresponding rotated EM density map is shown in the right panel, and the enlarged ribbon model showing a different rotational view to facilitate depiction of the interacting loops 1–3 from the αv-calf-1 with the single loop from the αv-thigh (left panel). The locations of the S546C and N685C mutations and the distance between them are indicated. Additional rotated views and locations of loops are shown in the lower middle and right panels. b, The sequence alignment of the amino acid loops of the αv-thigh and αv-calf-1 loops 1–3 of human αv with human αiib, α5 and α8 are shown. Red boxes indicate the location of S546C and N685C. Sequence conservation is indicated as follows: * fully conserved amino-acids, : strongly conserved amino-acids, . weakly conserved amino-acids. Putative residues participating in the loops interaction are indicated by +.
