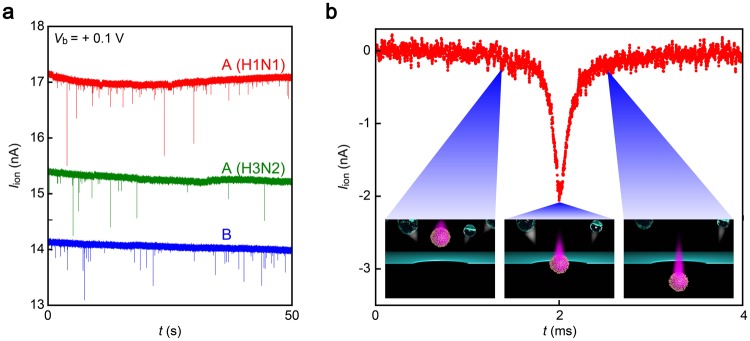
Figure 2.
Virion-derived resistive pulses. (a) Ionic current (Iion) traces recorded in chorioallantoic fluid containing A(H1N1) (red), A(H3N2) (green), or B (blue) using 300 nm-sized Si3N4 nanopore under the bias dc voltage Vb = +0.1 V. Each spike-like Iion change signifies electrophoretic translocation of single-virion through the pore channel. (b) A magnified view of a resistive pulse. The open pore current is offset to zero. Insets describe the viral motion upon transit through the conduit. Contaminants in the chorioallantoic solution depicted as transparent particles are repelled from the nanopore via electroosmotic flow during the virus sensing under the applied positive voltage.