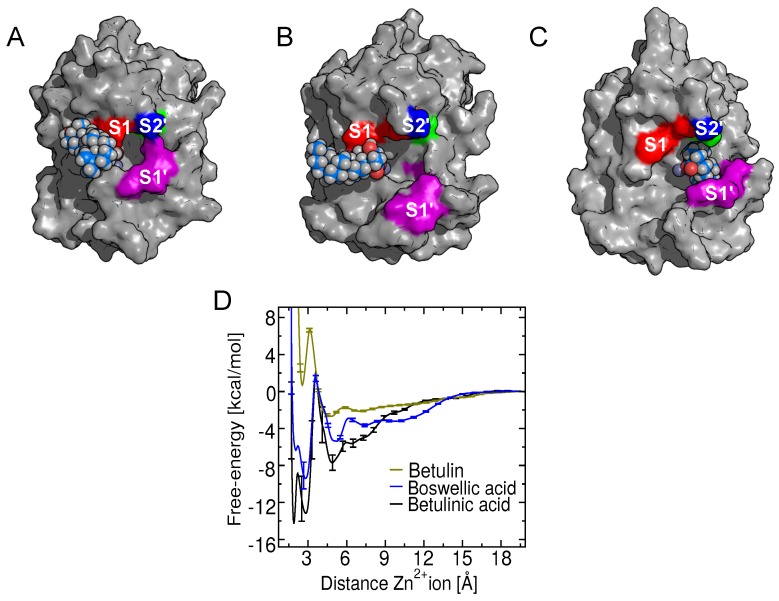
Figure 10.
Comparison of the potentials of mean force (Gibbs free-energy) and the binding poses of betulin and -boswellic acid with those of the most active compound betulinic acid. (A) Orientation of betulin associated with its free-energy minimum. The hydrophobic rings of betulin are interacting with the S1 subsite, without contact with the Zn ion. (B) Orientation of -boswellic acid associated with its free-energy minimum. (C) The orientation of bound betulinic acid is shown for reference. This compound fully occudes the S1 subsite. (D) Free energy as a function of the carboxylate-Zn ion distance for -boswellic and betulinic acid, or hydroxyl-Zn ion for betulin. The betulinic acid PMF is shown for comparison purposes.